Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Financial System: Faculty Facilitator: Rajesh Sadhwani
Uploaded by
parthshah1200Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Financial System: Faculty Facilitator: Rajesh Sadhwani
Uploaded by
parthshah1200Copyright:
Available Formats
INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM
Faculty Facilitator: Rajesh Sadhwani
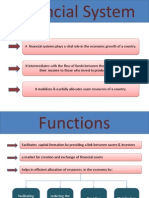
Financial System
Financial system play vital role in the economic growth of a country It intermediates between who the saves to who invest in productive assets Formal and informal financial system (Arbitrage Opportunity) Major advantages are
Low
transaction cost More transparency Minimize the default risk
Organized/Formal financial system comes under the MOF, SEBI, RBI and other regulatory bodies While Unorganized/informal financial system consists of
Individual
moneylenders Local bankers Traders Landlords Pawn Brokers
Organized Financial System
Components of Financial System
Financial
Institutions Financial Markets Financial Instruments Financial Services
Major categories of Financial Institutes are
Development
IDBI,
financial institutes (DFIs)
IFCI, SIDBI, NABARD, EXIM Bank etc
Non
banking financial companies (NBFC) Regulatory Bodies
SEBI,
RBI, IRDA etc
Housing
NHB,
finance companies (HFCs)
HUDCO, LICHF, HDFC, etc
Difference Between Banks & NBFC
1. 2. 3. 4.
5.
6. 7.
NBFC cannot collect deposits in the manner of a bank NBFC cannot issue checks drawn on itself NBFC cannot issue Demand Drafts like banks NBFC cannot indulge primarily in agricultural or industrial activity NBFC cannot engage in construction of immovable property NBFC cannot accept demand deposits While banks are incorporated under banking companies act, NBFC is incorporated under company act of 1956
Financial Markets
Financial Markets are a mechanism enabling participant to deal in financial claim Financial Market provide a facility where demand and requirement interact to set the price Types of Financial Markets
Primary
Markets (Primary market deals in new
issues) Secondary Markets (deals in outstanding / existing securities)
(OTC
Markets & Exchange Traded Market)
Financial Instruments
Financial Instrument is the claim against a person or an institution for payment at a future date a sum of money as interest or dividend. Financial Instruments differ in term of
Risk
Return Marketability
& liquidity type of option & transaction cost
Financial Services
Financial Intermediaries provide the key services like Merchant banking, Credit rating Leasing, Hire purchase Underwriting Portfolio management Depositories
Interaction Among the components
Financial institutes/intermediaries mobilize saving by issuing different type of financial instruments which are traded in financial markets. Financial institutes makes financial markets more liquid, stable & diversified.
Function of the Financial System
It serves as a link between savers and investors It provides payment mechanism for exchange of goods and services It provides a mechanism for the transfer of resources across geographic boundaries Financial system generates information, helpful in taking financial & economic decision Developed financial system lower the transaction cost It provides information to the operators/ players in the market such as individuals, business houses, Governments etc
Role of Financial Institutions (Intermediaries)
Financial Institutions provides
Liability
& assets transformation consisting of mobilizing of fund Provides large amount of loan on the basis of small deposits Risk transformation by acquiring diversification portfolio
Role of Financial Markets (Money Market)
A Money market is a short term debt instrument highly liquid Lesser transaction cost due to large denomination Provide a reasonable access to user of short term money Satisfies the liquidity needs of participants Provide base for the monetary authority Types of Money market instrument are
Call money Commercial Paper CBLO Treasury Bills Certificate of Deposits Repo, reverse repos, Notice money etc
Role of Financial Markets (Capital Market)
Capital Market is a market for long term securities Purpose of Capital market is to
Mobilize
the long term investments Provide capital in form of equity & debt to entrepreneurs Lower the cost of transaction & information Improve the efficiency of capital allocation through a comparative pricing mechanism.
Primary market & secondary markets Link between money market & capital market
Functions of Financial Markets
Separation, distribution and diversification of risk Efficient payment mechanism Providing information & track record about companies Enhancing the liquidity of financial claim through trading in securities Portfolio Management
Thank You
You might also like
- Business Plan TemplateDocument76 pagesBusiness Plan TemplateSlidebooks Consulting88% (34)
- Introduction to Financial MarketsDocument53 pagesIntroduction to Financial MarketsAddy Khan100% (1)
- CARREFOUR S.A. - Euro BondsDocument8 pagesCARREFOUR S.A. - Euro BondsSittipon'Seng'Samakkeenitch100% (4)
- Measuring and Interpreting Brand PerformanceDocument16 pagesMeasuring and Interpreting Brand PerformanceAdarsh Krishna100% (2)
- Relative Value Methodologies For Global Credit Bond Portfolio ManagementDocument13 pagesRelative Value Methodologies For Global Credit Bond Portfolio ManagementeucludeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Financial SystemDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Indian Financial SystemManoher Reddy100% (2)
- 10 Krugman PPT c13Document48 pages10 Krugman PPT c13Shehroze MoeenNo ratings yet
- 01-1 Indian Financial SystemDocument160 pages01-1 Indian Financial Systemanmaya agarwalNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Fundamentals: Why, how and what Products are traded on Financial Markets. Understand the Emotions that drive TradingFrom EverandFinancial Markets Fundamentals: Why, how and what Products are traded on Financial Markets. Understand the Emotions that drive TradingNo ratings yet
- (BNP Paribas) Smile TradingDocument9 pages(BNP Paribas) Smile TradingBernard Rogier100% (2)
- Financial Institution & Markets - Short NotesDocument41 pagesFinancial Institution & Markets - Short NotesGovind RathiNo ratings yet
- Bank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingFrom EverandBank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Financial Glossary Reuters PDFDocument241 pagesFinancial Glossary Reuters PDFPablo Bouvier100% (1)
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument26 pagesRole of Financial Markets and Institutionsshomy02No ratings yet
- A101 TurkeyDocument435 pagesA101 TurkeyDataGroup Retailer Analysis50% (6)
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument84 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsShreekumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Overview of Financial MarketsDocument35 pages1 Overview of Financial MarketsAiro RidhoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Financial MarketsUttam Gaurav100% (2)
- Basel - I, II, IIIDocument23 pagesBasel - I, II, IIISangram PandaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Importance of Financial SystemsDocument11 pagesNature and Importance of Financial SystemsAuie Eugene Frae SalameraNo ratings yet
- 1-Bond MarketDocument85 pages1-Bond Marketdharmtamanna80% (5)
- Customer Relationship Management and MarketingDocument41 pagesCustomer Relationship Management and MarketingharryworldNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument235 pagesMerchant BankingKarthikeyan Elangovan100% (1)
- An Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1Document16 pagesAn Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Indian Financial System - IntroductionDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Indian Financial System - IntroductionsejalNo ratings yet
- 1 Financial SystemDocument5 pages1 Financial SystemRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Afm PresentationDocument11 pagesAfm PresentationVipin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets & Institutions IntroductionDocument80 pagesFinancial Markets & Institutions IntroductionAnonymous LUvUBT60pnNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets ExplainedDocument33 pagesFinancial Markets ExplainedMaria KhalidNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviDocument85 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviinderpretationNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Market: (ACFN, 2 Credit Hour)Document25 pagesFinancial Institutions and Market: (ACFN, 2 Credit Hour)Mikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM OVERVIEWDocument28 pagesINDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM OVERVIEWRajEev ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial ServicesDocument346 pagesManagement of Financial ServicesHiral PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MBS FIMDocument16 pagesUnit 1 MBS FIMSarun ChhetriNo ratings yet
- CH1@FI&M Final EditedDocument7 pagesCH1@FI&M Final Editedtamiratg24No ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Services-1Document117 pagesFinancial Markets and Services-1Nagu BabuNo ratings yet
- JM ProjectDocument54 pagesJM Projectbhavesh25jadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Financial SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Indian Financial Systemapi-3739522100% (4)
- Finance Vs Financial SystemDocument61 pagesFinance Vs Financial Systempriyasumit100% (1)
- Financial Services Sector and Its Role in Expanding Economic OpportunityDocument29 pagesFinancial Services Sector and Its Role in Expanding Economic OpportunityDavid ThambuNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Put Your Notes Below The Unit of Your Portion. and Also Try Type/copy and Paste Your Part Instead of Pictures or Screenshots Unit-1Document76 pagesInstructions: Put Your Notes Below The Unit of Your Portion. and Also Try Type/copy and Paste Your Part Instead of Pictures or Screenshots Unit-1Diya MNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Financial System and Money MarketDocument28 pagesUNIT-1 Financial System and Money MarketashishNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets: Financial Markets (FMS) Are Organised and Highly RegulatedDocument12 pagesFinancial Markets: Financial Markets (FMS) Are Organised and Highly RegulatedShivain RoopraiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Financial System and Money MarketDocument28 pagesUNIT-1 Financial System and Money MarketashishNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Overview of Financial System - UAEDocument44 pagesModule 1 - Overview of Financial System - UAESonali Jagath100% (1)
- Indian Financial Systems: Meaning & ConstituentsDocument7 pagesIndian Financial Systems: Meaning & ConstituentsrishugNo ratings yet
- Function of Financial MarketsDocument22 pagesFunction of Financial MarketsPrabal Shrestha100% (1)
- Financial SystemDocument24 pagesFinancial Systemvinit.ambat13510No ratings yet
- Financial System: by Debraj (308) Avtar (304) Ajay (301) Pavani (306) TejaDocument20 pagesFinancial System: by Debraj (308) Avtar (304) Ajay (301) Pavani (306) Tejasinghbenipal93No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Markets: This Note Is Prepared by Prof Anita C Raman, For MBA Class of 2022, IBS HyderabadDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Financial Markets: This Note Is Prepared by Prof Anita C Raman, For MBA Class of 2022, IBS HyderabadSIDDHARTH GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial SystemsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Financial SystemsVinay ArtwaniNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument4 pagesIndian Financial SystemDivya BhadriNo ratings yet
- Financial AssignmemntDocument13 pagesFinancial AssignmemntSimeøn Cllåitøns ChungåNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument31 pagesFinancial MarketsCheesca Macabanti - 12 Euclid-Digital ModularNo ratings yet
- Session 1: Indian Financial SystemDocument12 pagesSession 1: Indian Financial SystemMahesh SatapathyNo ratings yet
- FMSDocument12 pagesFMSMahesh SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Index Executive Summary of Capital Markets Chapter 1 Investment BasicsDocument23 pagesIndex Executive Summary of Capital Markets Chapter 1 Investment Basicsswapnil_bNo ratings yet
- introduction to financial marketsDocument9 pagesintroduction to financial marketskirsurkulkarniNo ratings yet
- A Brief On Indian Financial SystemDocument9 pagesA Brief On Indian Financial Systemjai_tri007No ratings yet
- Hide 1 Financial Controls and Monitoring 2 Financial Services 3 See Also 4 References EditDocument21 pagesHide 1 Financial Controls and Monitoring 2 Financial Services 3 See Also 4 References EditPankaj GautamNo ratings yet
- Brokerage Services mfs-1Document28 pagesBrokerage Services mfs-1Abhi ShriNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Indian Financial SystemDocument29 pagesCH - 1 Indian Financial Systemtrupti_viradiyaNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument52 pagesFinancial Marketsdaksha pathakNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document62 pagesUnit 1Murugesan SNo ratings yet
- Financial System 1.zeroDocument86 pagesFinancial System 1.zerokhalifNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument14 pagesIndian Financial SystemAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Financial Market - HWDocument2 pagesFinancial Market - HWDanuta PiotrokaNo ratings yet
- Components of IFS NotesDocument6 pagesComponents of IFS NotesPrasad IngoleNo ratings yet
- Emmanuel GincbergDocument37 pagesEmmanuel GincbergLameuneNo ratings yet
- Stock Market in Australia: BY-Anil Vishnoi, 769Document20 pagesStock Market in Australia: BY-Anil Vishnoi, 769Kriti ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Strategic Planning and The Marketing ProcessDocument26 pagesChapter Two: Strategic Planning and The Marketing ProcessShamsyul AriffinNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Business MarketsDocument27 pagesAnalyzing Business Marketsermal88No ratings yet
- ChannelDocument10 pagesChannelVignesh LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Kinky Demand Curve ModelDocument11 pagesKinky Demand Curve ModelSiddharth JainNo ratings yet
- 02Document8 pages02Anubhav JainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Brand-Lecture NotesDocument125 pagesIntroduction To Brand-Lecture NotesCara_CNo ratings yet
- Parallel Financial SystemDocument2 pagesParallel Financial SystemBarkavi MaheshNo ratings yet
- Role of Advertising in Brand Promotion & AwarenessDocument18 pagesRole of Advertising in Brand Promotion & AwarenessJinu NamboodiriNo ratings yet
- 01-A Brief Introduction To The Colombo Stock MarketDocument4 pages01-A Brief Introduction To The Colombo Stock Marketmuthuraja83No ratings yet
- Depository SystemDocument33 pagesDepository SystemjasminalkaurNo ratings yet
- Cirque Du Soleil - Marketing AssignmentDocument1 pageCirque Du Soleil - Marketing Assignmentparaguai44No ratings yet
- Discount MarketDocument13 pagesDiscount MarketAakanksha SanctisNo ratings yet
- MARKETING MANAGEMENT TIPSDocument7 pagesMARKETING MANAGEMENT TIPSDebashish DasNo ratings yet
- 2003 Patriot Act Certification For Bank of AmericaDocument10 pages2003 Patriot Act Certification For Bank of AmericaTim BryantNo ratings yet
- Power Grid Fpo RHPDocument537 pagesPower Grid Fpo RHPGaurav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- International business strategiesDocument2 pagesInternational business strategiesSachu Shaolin0% (1)
- Sources of Funds 2Document30 pagesSources of Funds 2Tarun BishtNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie Selectiva - ReferatDocument2 pagesBibliografie Selectiva - ReferatCatrinel StanNo ratings yet