Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Liver Cancer: Primary Cancer of the Liver
Uploaded by
Mark James MelendresOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Liver Cancer: Primary Cancer of the Liver
Uploaded by
Mark James MelendresCopyright:
Available Formats
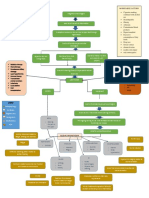
A primary cancer that arises in the liver, as oppose to cancer that spreads to the liver from other parts
of the body, known as liver metastases. Worldwide, it is fifth of the most common cancer, with highest incidence found in areas of China and Sub-Saharan Africa
HCC commonly develops in the presence of chronic liver cell injury, which produces inflammation, leading to hepatocyte regeneration and fibrosis. Repeated cycles of cell death and regeneration ultimately lead to cirrhosis, which is found in 60% to 80% of patients with HCC.
Chronic infections with Hep B virus and Hep C virus are the most important cause of liver damage worldwide. Long-term exposure to toxic chemicals is associated with HCC. Less common risk factors include certain genetic metabolic diseases, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, hereditary tyrosinemia, and antitrypsin deficiency. Aflatoxin B1 has the highest potency among the aflatoxins as a toxin and carcinogen. Chronic alcohol use is an important cause of cirrhosis
Abdominal pain Hepatomegaly Increasing abdominal girth secondary to ascites Anorexia Weight loss Hepatic arterial bruits Jaundice
Splenomegaly Fever Weakness and nonspecific symptoms Paraneoplastic syndromes (hypoglycemia, erythrocytosis, hypercalcemia, hyperthyroidism, hypercholesterolemia, carcinoid syndrome)
Center on the prevention of chronic liver damage and cirrhosis. Universal vaccinations of newborns against HBV in endemic areas may dramatically reduce incidence. Interferon - E is an approved treatment to reduce both liver damage and the onset of cirrhosis in chronic HBV, as well as prevent the development of HCC.
Refrigerated storage and transportation of food grains should reduce the rate of ingestion of aflatoxins. Continued efforts to reduce chronic alcohol abuse is also important. Screening high-risk individuals with annual ultrasounds and obtaining an Efetoprotein tumor marker every 4 months has helped to identify HCC at early stages.
High risk patients with elevated AFP levels and patients seen with clinical features of HCC should undergo a high-speed helical CT scanning, allowing threedimensional reconstitution and vascular imaging w/o invasive angiography. (Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is more sensitive)
Transcutaneous ultrasonography can be used to identify liver lesions, guide percutaneous biopsy, and provide treatment by direction injection or ablation techniques. Intraoperative ultrasound can determine the number and extent of lesions, as well as the association of intrahepatic arteries and veins. Laparoscopic ultrasound probes can exclude the presence of extra hepatic disease on perotonial surfaces.
Common sites for distant metastases from HCC, which usually develop late in the disease course, are the lung, bone, and the adrenal glands. Recurrent or progressively enlarging liver lesions are serious conditions , since they greatly affect the liver function. Death usually occurs due to liver failure, fatal bleeding, tumor rupture, or esophageal varices.
Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
PREVENTIVE MANAGEMENT Note if client works in high risk occupation. Assess for exposure to contaminated food or poor sanitation practices by food service workers. Determine presence of condition noting whether problem is acute or chronic.
Stress importance of responsible drinking or avoiding alcohol, when indicated. Identify signs/symptoms that warrant prompt notification of health care provider. Encourage client with liver dysfunction to avoid fatty foods. Discuss safe use/concerns about clients medication regimen, certain cardiovascular drugs, antidepressants.
Refer to specialist/liver treatment center, as indicated. Discuss the need for vaccination, as indicated. Discuss the appropriateness of prophylaxis immunizations. Refer to community resources, drug/alcohol treatment program, as indicated.
Acute pain related to side effects of therapeutic agents as evidenced by verbal report of pain. Imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements related to interference of metabolism of nutrients and amino acids as evidenced by weight loss.
You might also like
- Liver CancerDocument44 pagesLiver CancerJoyce Ann CumlatNo ratings yet
- Management of Liver SecondariesDocument36 pagesManagement of Liver SecondariesSasi Kumar100% (1)
- Solid Liver Lesions - Differential Diagnosis and Evaluation - UpToDateDocument25 pagesSolid Liver Lesions - Differential Diagnosis and Evaluation - UpToDateElisa FloresNo ratings yet
- HBV HCV Cirrhosis Gender Perinatal Transmission Age Family HX RaceDocument2 pagesHBV HCV Cirrhosis Gender Perinatal Transmission Age Family HX RaceKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- A Man With Prostate Cancer: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageA Man With Prostate Cancer: Nursing Care PlanmolecolareNo ratings yet
- Liver ImagingDocument7 pagesLiver ImagingBenn BerriganNo ratings yet
- Canadian Task Force Prostate CancerDocument13 pagesCanadian Task Force Prostate CancerarthurmathieuNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperthropyDocument54 pagesBenign Prostatic HyperthropyPrawira Buntara PutraNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer OverviewDocument22 pagesCervical Cancer OverviewnyseaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Ca Flow ChartDocument5 pagesProstate Ca Flow ChartDanekka TanNo ratings yet
- Triple Negative Breast CancerDocument15 pagesTriple Negative Breast CancerUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument8 pagesProstate CancerJohnNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and SpleenDocument19 pagesGallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and Spleensarguss14100% (3)
- UTI LectureDocument62 pagesUTI LectureHaidar ShiddiqNo ratings yet
- Nderstand - Bc/statistics: Leer Esta Página en EspañolDocument6 pagesNderstand - Bc/statistics: Leer Esta Página en EspañolMonica Shendy100% (1)
- 8 Parasitic Adaptations in HelminthsDocument60 pages8 Parasitic Adaptations in Helminthsapi-3732735100% (4)
- Urinary Tract Infections PowerpointDocument22 pagesUrinary Tract Infections Powerpointsamdhathri100% (1)
- Prostate CancerDocument4 pagesProstate CancerNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Željko Puljiz, MD., PHDDocument67 pagesŽeljko Puljiz, MD., PHDpuljiz7No ratings yet
- Elimination Pattern (Fecal) MSPDocument20 pagesElimination Pattern (Fecal) MSPMuhammadNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument231 pagesCancerJoshua EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Trans Urethral Resection of The ProstateDocument8 pagesTrans Urethral Resection of The ProstateKath RecNo ratings yet
- Calcium and Phosphorus HomeostasisDocument3 pagesCalcium and Phosphorus Homeostasisshakila786No ratings yet
- Epidemiology & of Cancer in India: EtiologyDocument20 pagesEpidemiology & of Cancer in India: Etiologysuman singhNo ratings yet
- Myelofibrosis: Heri SutrisnoDocument24 pagesMyelofibrosis: Heri SutrisnoDestrini Anjani LandaNo ratings yet
- Scrotal Disease - 2Document47 pagesScrotal Disease - 2Hillary BushnellNo ratings yet
- The Breast: AnatomyDocument3 pagesThe Breast: AnatomyRyan James Lorenzo Miguel50% (2)
- Breast Cancer FactsDocument2 pagesBreast Cancer FactsScott CoursonNo ratings yet
- Colon Cancer: Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesColon Cancer: Risk FactorsAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Management of IncontinenceDocument91 pagesManagement of IncontinenceVahid Msmi100% (1)
- Chirosis HepaticDocument8 pagesChirosis HepaticCikalHrNo ratings yet
- Palliative EnciesDocument96 pagesPalliative EnciesnandanNo ratings yet
- By: Vismin Prince Magno: Liver CancerDocument17 pagesBy: Vismin Prince Magno: Liver Cancerhedokido100% (1)
- Cancer: Causes and Risks FactorsDocument88 pagesCancer: Causes and Risks FactorsClancy Anne Garcia NavalNo ratings yet
- What Is Pancreatic CancerDocument12 pagesWhat Is Pancreatic CancerissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Bladder Training PDFDocument5 pagesBladder Training PDFDjfnswn UkhtyNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Types and UsesDocument6 pagesIV Fluid Types and UsesKiara Denise TamayoNo ratings yet
- Test Report Gupta DiagnosisDocument17 pagesTest Report Gupta Diagnosisdrblgupta1973100% (1)
- Lesson 7 - Organ TransplantationDocument14 pagesLesson 7 - Organ Transplantationapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Molecular Pathology of Breast CancerDocument42 pagesMolecular Pathology of Breast CancerleartaNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument7 pagesUniversity of Northern PhilippinesRc Peralta Adora100% (1)
- Varian Cysts: The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument4 pagesVarian Cysts: The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and GynecologyAde Gustina SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Know Which Vitamin Helps in Blood ClottingDocument11 pagesKnow Which Vitamin Helps in Blood ClottingGoranNo ratings yet
- Cancer NursingDocument53 pagesCancer Nursingfairwoods100% (1)
- Prostate Biopsy - UpToDateDocument47 pagesProstate Biopsy - UpToDateCésar Aguirre RomeroNo ratings yet
- Management Bladder IncontinanceDocument14 pagesManagement Bladder IncontinancepaswordnyalupaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Hepatic Failure: Presented By: Sandhya Harbola M.SC Nursing 1 Year PcnmsDocument54 pagesPresentation On Hepatic Failure: Presented By: Sandhya Harbola M.SC Nursing 1 Year PcnmsShubham Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaDocument7 pagesAdenoid Cystic CarcinomalonadiolandaNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer ScreeningDocument12 pagesBreast Cancer ScreeningCare Diagnostic CenterNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The EsophagusDocument31 pagesCancer of The EsophagusBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- DRTP Sample QuestionsDocument6 pagesDRTP Sample QuestionsDeepthi SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Created By: Katherine L. Laud, SNDocument31 pagesCreated By: Katherine L. Laud, SNKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Prostate Specific AntigenDocument7 pagesProstate Specific Antigenariefritonga2010No ratings yet
- How to Do Breast and Testicular Self-ExamsDocument33 pagesHow to Do Breast and Testicular Self-ExamsMaJo GuanteroNo ratings yet
- Bone Density TestDocument6 pagesBone Density Testtharia786No ratings yet
- Fatty Liver and Cirrhosis - DR GurbilasDocument7 pagesFatty Liver and Cirrhosis - DR GurbilasDr. Gurbilas P. SinghNo ratings yet
- Cytology Proposed Plan - ProjectDocument23 pagesCytology Proposed Plan - ProjectRogers256No ratings yet
- PET CT Principles PDFDocument28 pagesPET CT Principles PDFIonuț RusNo ratings yet
- What You Can Do to Prevent Cancer: Practical Measures to Adjust Your Lifestyle and Protect Your HealthFrom EverandWhat You Can Do to Prevent Cancer: Practical Measures to Adjust Your Lifestyle and Protect Your HealthNo ratings yet
- Liquid Biopsy in Urogenital Cancers and its Clinical UtilityFrom EverandLiquid Biopsy in Urogenital Cancers and its Clinical UtilitySeyed Mohammad Kazem AghamirNo ratings yet
- Modified Diet Consistency Group 1Document34 pagesModified Diet Consistency Group 1Mark James Melendres50% (4)
- Diet Modified in CompositionDocument36 pagesDiet Modified in CompositionMark James Melendres100% (1)
- Case Analysis Pre Eclampsia.. :DDocument27 pagesCase Analysis Pre Eclampsia.. :DMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Treatment of Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesPathophysiology and Treatment of Tetralogy of FallotMark James Melendres100% (12)
- Interview With CouplesDocument2 pagesInterview With CouplesMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument1 pageDrug Study FormatMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument1 pageNCP FormatMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Nurse's PrayerDocument1 pageNurse's PrayerMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 2003 EditedDocument7 pagesChapter 4 2003 EditedMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Verification LetterDocument1 pageVerification LetterMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Gordons Sa Celiac DiseaseDocument4 pagesGordons Sa Celiac DiseaseMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- My Name Is KhanDocument1 pageMy Name Is KhanMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Song About Bowel CancerDocument2 pagesSong About Bowel CancerMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- C2. Informed Consent Authorization - 2003Document1 pageC2. Informed Consent Authorization - 2003Mark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Patho of Post Renal Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPatho of Post Renal Acute Renal FailureMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Summary of Capacity Per YearDocument13 pagesSummary of Capacity Per YearMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Reliability Coefficient FormulaDocument11 pagesReliability Coefficient FormulaMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- C3. Parent's Consent - 2003Document1 pageC3. Parent's Consent - 2003Mark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Written Report NutriDocument7 pagesWritten Report NutriMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Requesting Burn Patient Records for Nursing ResearchDocument2 pagesRequesting Burn Patient Records for Nursing ResearchMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Tele IcuDocument1 pageTele IcuMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Minors Assent - 2003Document1 pageMinors Assent - 2003Mark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy CaseDocument6 pagesAppendectomy CaseMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument1 pageFetal CirculationMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Tingkat KesadaranDocument16 pagesTingkat KesadaranShinta NurjanahNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument11 pagesMalariaWynli Fullo AncogNo ratings yet
- Workplace EmergenciesDocument39 pagesWorkplace EmergenciesUpul Nishantha ThalpawilaNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases of Leafy GreensDocument6 pagesCommon Diseases of Leafy GreensAgung PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Spartan Bodyweight WorkoutsDocument102 pagesSpartan Bodyweight WorkoutsSamir DjoudiNo ratings yet
- Ageism PowerpointDocument11 pagesAgeism Powerpointapi-254132646No ratings yet
- BDD Fact SheetDocument2 pagesBDD Fact SheetKeen ZeahNo ratings yet
- Strupp ArticleDocument10 pagesStrupp ArticleDental SpaNo ratings yet
- Home Economics LiteracyDocument43 pagesHome Economics LiteracyAndrea Fidel Raymundo100% (3)
- Transmission Substation Work Practice Manual 2016-07-22Document499 pagesTransmission Substation Work Practice Manual 2016-07-22Edmund YoongNo ratings yet
- Autism Case Report on 3-Year-Old MaleDocument24 pagesAutism Case Report on 3-Year-Old MaleMichael John CanoyNo ratings yet
- SGLGB Form 1 Barangay ProfileDocument3 pagesSGLGB Form 1 Barangay ProfileMark Lenon Par Mapaye100% (1)
- Fitness WalkingDocument60 pagesFitness WalkingJC LeriaNo ratings yet
- Wellness massage exam questionsDocument3 pagesWellness massage exam questionsElizabeth QuiderNo ratings yet
- A Plant-Growth Promoting RhizobacteriumDocument7 pagesA Plant-Growth Promoting RhizobacteriumdanyjorgeNo ratings yet
- Anarchy RPG 0.2 Cover 1 PDFDocument14 pagesAnarchy RPG 0.2 Cover 1 PDFanon_865633295No ratings yet
- Handbook of Laboratory Animal Science - Vol IIIDocument319 pagesHandbook of Laboratory Animal Science - Vol IIICarlos AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument10 pagesFoundationBardoNo ratings yet
- Dental Restorative Digital Workflow: Digital Smile Design From Aesthetic To Function PDFDocument12 pagesDental Restorative Digital Workflow: Digital Smile Design From Aesthetic To Function PDFCamilo GuerreroNo ratings yet
- MG English Consumer BookletDocument41 pagesMG English Consumer BookletAnh HoaiNo ratings yet
- Lasik VisionDocument3 pagesLasik VisionPrachurya SarmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment 1Document70 pagesNursing Assessment 1Amira AttyaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System ExplainedDocument33 pagesThe Digestive System ExplainedGulAwezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric PharmacotherapyDocument4 pagesPediatric PharmacotherapyRiriNo ratings yet
- Tugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI (Revisi) - Rizka Amalia Hutami - 150510160235Document2 pagesTugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI (Revisi) - Rizka Amalia Hutami - 150510160235RizkaNo ratings yet
- The Process of Grief PDFDocument6 pagesThe Process of Grief PDFnicoletagr2744100% (1)
- A Case of Eclectic Family TherapyDocument88 pagesA Case of Eclectic Family Therapygun gorNo ratings yet
- Methods of Investigating Brain and LanguageDocument12 pagesMethods of Investigating Brain and Languagekiranjit_123100% (2)
- Environmental Hazards For The Nurse As A Worker - Nursing Health, & Environment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Hazards For The Nurse As A Worker - Nursing Health, & Environment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFAgung Wicaksana100% (1)
- EV3110 SIA Group ReportDocument38 pagesEV3110 SIA Group ReportWill MyatNo ratings yet