Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics of The Eye
Uploaded by
Princess Dianna SulitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics of The Eye
Uploaded by
Princess Dianna SulitCopyright:
Available Formats
Lens Maker Equation
1 2
1 1 1
( 1)( ) n
f R R
= +
Thin Lenses in Contact
1 2
1 1 1
f f f
= +
R and f are + if convex, - if concave.
Examples:
1. A plano-convex lens is made of glass of
index of refraction equal to 1.5. The curved
surface has a radius of 20cm. What is the
focal length of the lens?
2. A double concave lens is made of glass
(n=1.5) and has a focal length of 30cm. If
the radius of one of the surfaces is 30cm,
find the radius of the other surface.
3. What is the resulting focal length and power if
two thin lenses each of focal length +25cm
are in contact?
4. An object 0.3m from a lens gives a virtual
image 0.1m from the lens. What is the focal
length and nature of the lens?
5. The focal length of a lens is 5cm. How far
must the lens be adjusted from the screen to
produce a clear image of a) an object that 2m
away b) a distant object?
6. How far from a converging lens (f =15cm)
must an object be placed in order to produce
an image that is a) inverted and magnified
three times b) upright and magnified three
times?
7.A converging lens has a focal length of
8cm. An object is located 14.0cm in front
of this lens. A second converging lens of
the same focal length is located 20cm to
the right of the first lens. Relative to the
second lens, where is the final image?
Obtain over all magnification.
8. A converging lens (f=12cm) is located
30cm to the left of a diverging lens 9f=-
6.0cm). An object is located 36cm to the
left of the converging lens. Locate the final
image relative to the diverging lens.
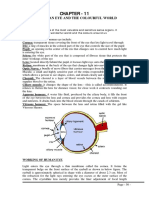
The Physics of the Eye
The eye is an opaque ball averaging 2.3cm in diameter
Parts of the Eye
Cornea- outer thin transparent membrane
of the eyeball. The cornea serves to protect
the eye and refract most of the incident light.
Pupil-The black circle that we see in the
middle of the eye. The pupil is actually an
opening through light enters the inner portion
of the eye. It changes its size to regulate
amount of light entering the eye.
Iris- the colored circle of the eye.
It may be brown, black, gray and others
depending on race.
Its main task is to regulate the size of the
pupil by contraction or relaxation of its
muscles.
It has been claimed that each iris is unique
and is a better identifier than the
fingerprints
Trivia:. Iridology is the study of the iris of
the eye. The iris is divided into 40 zones,
each corresponding to different body parts
and that diseases of different body parts
may be diagnosed by mere looking at the
iris.
Ignatz Von Peczely(1866) father of
iridology.
Sclera-The white background of the
eye. It provides structure, protection and
strength to the eye.
Crystalline lens clear convex structure at
the back of pupil. It can focus objects are
different distances by changing its shape.
This ability of the lens is called
accommodation.
The ciliary muscles are attached to the
crystalline lens and are responsible for
changing the shape of the lens when
focusing objects at different distances. To
focus on a nearby object, the muscles
contract and the center of the lens are
thicker. If the object is distant, the muscles
are relaxed and the lens is thin.
ACCOMMODATION
Retina
1. For normal vision, the image of an
object seen by the eye is formed exactly at
the retina.
2. The retina consists of light sensitive
rods and cones. The cones can distinguish
color and are responsible for our daytime
vision. On the other hand, the rods enable
us to see in the dark
Fovea- the region of most distinct vision.
There are about 200,000 cones but no
rods in the fovea.
Blind Spot-the point in the retina where the
optic nerves exit is called the blind spot.
The optic nerve carries images from the
retina to the brain.
The Blind Spot Experiment
Close your left eye and look at the figures in this box with your right eye only.
You can see both the square and the circle. Try moving this book slowly
towards your face. You will reach a certain distance where the circle
disappears. Does the same thing happen when you repeat the procedure
using the left eye?
aqueous humor located between the
cornea and lens
vitreous humor located after the lens
Both humors are responsible for gioving
the eye its near perfect spherical shape.
They also belong to the refractive system
of the eye.
Do you know that your eyes reveal
your emotions?
20/20 vision
Visual acuity simply means clarity of vision
or sharpness of vision.
It is expressed usually as a fraction. The
numerator is the standard testing distance, 20
feet in almost all countries and 6meters in
Britain. The denominator represents the
distance in feet or meters at which a person with
normal vision is able to see clearly an object
seen by another at 20 feet or 6meters.
If your vision is 20/50, you can see at 20 ft
what a normal vision man can see at 50 ft.
Hawks for instance have 20/2 vision.
Legal blindness is usually defined as
visual acuity less than 20/200 with
corrective lenses
VISUAL ACUITY
EYE DEFECTS
The closest distance at which an object
can be seen clearly by the eye is called
the near point of the eye. The near point
for young adults with normal vision is 25
cm, for children around 10 cm and for the
aged, 50 cm or more.
(www.main.com/~gj/physics/an
na/)
LEONARDO DA VINCI
While it is true that his
masterpieces like Mona Lisa,
Madonna of the Rocks and
The Last Supper have brought
him fame, his many sketches
and notes have been the basis
of modern scientific inventions.
He was the originator of the
concept of contact lens. In
1508, he sketched and
described several forms of
contact lenses though not
producing even one for testing.
The far point of the eye is the farthest
distance at which an object can be
seen clearly. The far point of the normal
eye is taken as infinity.
Thus, a normal healthy eye can see
objects as close as 25cm or very distant
from it.
Myopia is the medical term for
nearsightedness. People suffering from
this visual problem can see close objects
clearly but the distant ones are blurred.
A myopic eye forms the image of a distant
object in front of the retina because the
eyeball is longer than the normal or too
curved.
This can be corrected by using a diverging
lens.
The far point of a person is 2.0m away rather
than infinity. What corrective lens should be
prescribed? What should be the power of this
lens?
A persons right eye is corrected by a 4.0D
lens, worn 1.8 cm from the eye. A) Is the person
nearsighted or farsighted? B) What is this
persons near point without glasses? C) What is
his far point without glasses? D) Suppose he
decided to use contact lens instead of
eyeglasses, what should be the power of the
corresponding contact lens?
A person suffering from hypermetropia
(hyperopia in some books) or
farsightedness can see distant objects but
can not focus clearly on nearby objects. In
this case, the eyeball is too short and the
image of a close object is formed behind
the retina. A converging lens can correct
this problem.
A farsighted person has a near point
located 210cm from the eyes. Determine
the power of the lens to be used.
People aged 40 and above are suffering from
presbyopia. Presbyopia is sometimes called the
aging eyes or old eyes in as much as it is a normal
consequence of growing old and cannot be
prevented. As we grow old, the crystalline lens hardens
and the ciliary muscles become less flexible making
accommodation not as easy as before. As a result of
this, distant objects are seen clearly, but nearby objects
are not. We see elderly people holding a newspaper at
arms length to read it. A presbyopic eye needs reading
glasses. Alternatively, a bifocal lens may be prescribed.
The upper half of a bifocal lens is for normal viewing
while the lower half is for reading purposes. A line
separates the upper from the lower half. A bifocal lens
produces the so called split- image effect and reveals
the age of the user. To eliminate these, a no-line bifocal
lens or progressive lens may be used.
A person suffering from astigmatism
cannot focus simultaneously on horizontal
and vertical lines. The corneas having
unequal curvature in various directions
causes this. A cylindrical lens is used to
correct astigmatism.
Pinhole Glasses
Introduced in 1995, pinhole glasses or stenopeic
glasses are not made of glasses but of opaque
material containing holes about 1.0mm in
diameter. Pinhole glasses are said to correct
refractive errors by admitting only those rays that
pass through the central portion of the pupil .
Laser vision surgery has been a popular
procedure to correct eye defects. PRK
(Photorefractive Keratectomy) and LASIK (Laser
Assisted in-situ Keratomileusis) use the excimer
laser to reshape the cornea so that images are
formed at the retina. The procedures take
approximately 10 minutes, with actual laser time
exposure varying from 15 to 60 seconds. People
who have undergone this surgery feel no pain
but may experience a foreign body sensation
lasting for several hours (LASIK) and 3 to 4 days
(PRK).
LASIK
Laser Assisted In-Situ Keratomileusis
Bionic Eye
It comprises a computer chip that
sits in the back of the individual's
eye, linked up to a mini video
camera built into glasses that they
wear.
Images captured by the camera
are beamed to the chip, which
translates them into impulses that
the brain can interpret
COMPARISON BETWEEN EYE AND CAMERA
EYE CAMERA
1. Opening for light to
enter
Pupil Aperture
2. Regulation of size of
opening
Muscles of the iris Diaphragm
3. Refracting system Cornea, lens, vitreous
and aqueous humor
Biconvex lens
4. Where image is
formed
Retina Film
5. Regulation of time of
exposure to light
eyelid shutter
6. Focusing mechanism Ciliary muscles change
the shape of lens
Digital Camera
A digital camera captures the image through a
sensor composed of array of electrodes or
photosites. The image sensor can be a charge
coupled device (CCD) or complementary metal
oxide semiconductor (CMOS). The sensor
converts light to electrical signals. The signals
are converted into binary number by means of
an analog to digital converter, processed by a
built in computer and stored in a memory card in
JPEG or TIFF format.
The first consumer-oriented digital cameras
were sold by Kodak and Apple in 1994.
CMOS image sensor
( Source: How Stuff
Works)
Both CCD and CMOS image sensors convert light into electrons
CCD sensor (Source: How
Stuff Works)
Magnifier and Compound
Microscope
A magnifying glass is simply a
converging lens that produces a virtual,
upright and enlarged image of an
object placed at a distance less than its
focal length.
The angular magnification M of a magnifier
is defined as the ratio of the angular size
of the image it produces to the angular
size of the object placed at the near point
and viewed by a naked eye.
p h
p h
M
cm 25
cm 25 /
/
tan
' tan '
= = ~ =
u
u
u
u
But 1/p = 1/f 1/d
i
. Since the image formed by
the magnifying glass is virtual, the image
distance q must be negative. Thus, 1/p = 1/f +
1/d
i
. Substituting this in the equation for
angular magnification
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
i
d f
M
1 1
cm 25
Both f and q must be in centimeters.
If the object is viewed at a distance equal to
the focal length, the image is formed at infinity.
f
M
cm 25
=
For an image formed at 25cm,
1
cm 25
+ =
f
M
*A short focused lens produces greater magnification than
long focused lens.
*Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek,the father of microbiology, is
said to have produced a magnifying glass from glass
bead with a magnification of 275.
A biologist examines a specimen using a
simple magnifier of power 12D. What is
the angular magnification if the final image
is produced at a) infinity b) at the normal
near point of the eye?
Compound Microscope
Magnifying glass with an additional lens.
Objective-
* lens near the object to be viewed,
* pre-magnifies the object by producing
a real, inverted and enlarged image.
This image becomes the object for the
eyepiece.
Eyepiece-
* magnifying glass, lens near the eye
*produces an enlarged, virtual and upright
final image.
The compound microscope was believed to be
invented by the father and son team of Hans and
Zacharias Jannsen in 1590
To obtain large magnification, the object is placed at a
distance approximately equal to the focal length of the
objective (f
o
).
Also, compound microscopes are designed so that the
eye is fully relaxed when viewing the final image. A
necessary condition for this is that the final image must
be very far from the eyepiece or at infinity. This will only
be true if the first image formed by the objective fall just
inside the focal point of the eyepiece. If the objective
and the eyepiece were separated by a distance L, it
follows that the distance of the first image from the
objective is L f
E
, where f
E
is the focal length of the
eyepiece. The magnification produce by the objective
and the eyepiece are respectively
Magnification by a Compound Microscope
E
o E
o E
and
L f q 25
M M
p f f
| |
= = =
|
\ .
Final Magnification M
E
o E
o E
L f
M M M 25
f f
| |
= =
|
\ .
Greater magnification is achieved by using short focused
objective and eyepiece lenses.
Antoni van Leeuwenhoeks simple microscope. The object being
examined was fixed to the spike and viewed through a single
converging lens. (Source: Grolier International Encyclopedia)
A compound microscope is to be
constructed using a 0.4cm focal length
objective and a 3.0cm focal length
eyepiece. The two lenses are separated
by 20.0 cm. A) Determine the angular
magnification of microscope B) Compare
this magnification with the maximum
angular magnification obtainable with the
eyepiece alone as a magnifying glass.
Telescope
A telescope is device that enables us to see
distant object. There are two types of telescope:
refracting and reflecting telescope.
A refracting telescope makes use of lenses for
its objective and eyepiece. A reflecting telescope
uses a concave mirror, instead of a converging
lens, as the objective.
History claims that the telescope was
accidentally invented by a Dutch
lensmaker Hans Lippershey in 1608 when
he looked at a distant church using two of
his converging lenses. He called his
invention look glass and applied for a
patent. However, he was denied because
it was too simple that everyone knows it
during his time.
Galileos far looker uses a converging
lens for the objective and a diverging lens
for the eyepiece.
For the objective: object distance is at infinity.Hence the
first image is formed just beyond the principal focus of
the objective. This first image is real, inverted and
smaller.
For the eyepiece: The image formed by the objective
normally lies just inside the focal point of the eyepiece.
The eyepiece, acting like a magnifying glass, produces a
magnified virtual final image at infinity.
The distance between the two lenses is therefore the
length of the telescope and is equal to the sum of the
focal lengths of the two lenses.
The angular magnification of the telescope is the ratio of
focal length of the objective to that of the eyepiece.
o
E
f
M=-
f
A physics student was tasked to make a
telescope out of old glass lenses having
these focal lengths: 4.0cm, 8.0cm, 9.0cm,
12.0 cm and 16.0cm. Which combination
will produce the maximum magnification?
What is this maximum magnification?
Hubble Space Telescope launched on April
25, 1990 (Source NASA)
You might also like
- Method Statement (RC Slab)Document3 pagesMethod Statement (RC Slab)group2sd131486% (7)
- Optical Math Handout RJohnson PDFDocument5 pagesOptical Math Handout RJohnson PDFRitesh Upadhyay100% (1)
- Lab 10 - Law of ReflectionDocument2 pagesLab 10 - Law of Reflectionapi-408463795100% (1)
- Alugbati Plant Pigment Extraction As Natural Watercolor SourceDocument6 pagesAlugbati Plant Pigment Extraction As Natural Watercolor SourceMike Arvin Serrano100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Corrective LensesDocument24 pagesChapter 6 Corrective LensesSoorav MlicNo ratings yet
- 11.human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument19 pages11.human Eye and Colourful WorldJagpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Thick LensDocument51 pagesThick LensRiska Lidia100% (1)
- Ray Optics (Theory)Document20 pagesRay Optics (Theory)Kumar Rohit100% (1)
- Curved Mirror & Thin Converging LensDocument38 pagesCurved Mirror & Thin Converging LensAndrewD2404100% (1)
- Contact Lenses 1: by Hatem S.H. Barhoom MHSC (Clinical Optometry) UKM - MalaysiaDocument250 pagesContact Lenses 1: by Hatem S.H. Barhoom MHSC (Clinical Optometry) UKM - MalaysiaHasan Ansari100% (1)
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-II (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Document18 pagesSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-II (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- Refractive Errors: Dr. Leow Thye YngDocument55 pagesRefractive Errors: Dr. Leow Thye YngRaissaNo ratings yet
- Optics ReviewerDocument14 pagesOptics ReviewerLeny LacsonNo ratings yet
- What Is Retinoscopy?: Myopia HyperopiaDocument4 pagesWhat Is Retinoscopy?: Myopia HyperopiababyswitNo ratings yet
- Our Eye As A Camera Refraction, Errors and Solutions.: DR - Ali.A.Taqi Fifth Year StudentsDocument44 pagesOur Eye As A Camera Refraction, Errors and Solutions.: DR - Ali.A.Taqi Fifth Year Studentsabigail100% (1)
- Optics-Hecht - 03-Chap4-The Propagation of Light - OKDocument45 pagesOptics-Hecht - 03-Chap4-The Propagation of Light - OKfara latifa100% (2)
- Lens & MirrorDocument8 pagesLens & Mirrordivya singh100% (1)
- Prescribing Lenses - Troubleshooting .Document65 pagesPrescribing Lenses - Troubleshooting .KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Optics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesDocument46 pagesOptics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesBrianna Malcolm100% (1)
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionANJALI RANANo ratings yet
- Optics Revision DR - GhadaDocument17 pagesOptics Revision DR - Ghadamohamed abo elnor100% (1)
- Lenses: - Lenses Are Made of A Material: Glass, Quartz, EtcDocument5 pagesLenses: - Lenses Are Made of A Material: Glass, Quartz, EtcADimas Cahyaning FurqonNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument25 pagesOpticsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- CP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionDocument4 pagesCP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionRashed AlawaishehNo ratings yet
- Review: True or FalseDocument18 pagesReview: True or FalseAdorio JillianNo ratings yet
- Spherical LensesDocument16 pagesSpherical LensesJúnior AlvesNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For PodcastDocument74 pagesOptics and Refraction For PodcastKittithep Sukkhong100% (1)
- Refraction Through A Lens PDFDocument3 pagesRefraction Through A Lens PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Orientation, History Taking and ExaminationDocument77 pagesOrientation, History Taking and ExaminationMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Lens &prismDocument16 pagesLens &prismJulian Massey100% (1)
- Grometrical Optics (With Solution)Document250 pagesGrometrical Optics (With Solution)Lalit Sharma100% (1)
- Concave and Convex LensDocument7 pagesConcave and Convex LensannmarieNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Questions #4 - LensDocument4 pagesFinal Exam Questions #4 - Lensanonslu2012No ratings yet
- OculomotorDocument41 pagesOculomotorcmirceaNo ratings yet
- ENTOPTIC-PHENOMENON Wih BordersDocument5 pagesENTOPTIC-PHENOMENON Wih BordersEdrese Aguirre0% (1)
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Introduction To Spherical Lenses2Document6 pagesIntroduction To Spherical Lenses2Nuon HudaNo ratings yet
- Thick Lens:: Optics 1 - by Dr.H.Huang, Department of Applied Physics 1Document16 pagesThick Lens:: Optics 1 - by Dr.H.Huang, Department of Applied Physics 1Shweta DixitNo ratings yet
- Previous Question Paper 1 DOADocument8 pagesPrevious Question Paper 1 DOAMahesh BodaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument66 pagesGeometrical OpticsLalith Kumar Reddy Vedium100% (1)
- 10 LightDocument50 pages10 LightNaveen Kumar100% (1)
- Eyeglasses Presbyope PDFDocument10 pagesEyeglasses Presbyope PDFmickaz100% (1)
- Class Xii - CH-9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks WiseDocument37 pagesClass Xii - CH-9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks Wisesamaran270s100% (1)
- Biophysics Module 4 Principles of Optics in Biological Studies andDocument50 pagesBiophysics Module 4 Principles of Optics in Biological Studies andJohn Mark Gallano Canayon100% (1)
- Investigation in OptometryDocument10 pagesInvestigation in Optometryrapid73No ratings yet
- Eyes On Eyecare - 2021 - Dry Eye ReportDocument28 pagesEyes On Eyecare - 2021 - Dry Eye ReportEsther AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument7 pagesLight - Reflection & RefractionManya Juneja100% (1)
- 1628598558881SYBSC Physics Paper 2 - Optics MCQs With AnswersDocument27 pages1628598558881SYBSC Physics Paper 2 - Optics MCQs With AnswersShivam VermaNo ratings yet
- Intraocular Lens: Evolution, Types & UsesDocument63 pagesIntraocular Lens: Evolution, Types & UsesSriniwas100% (1)
- Ray OpticsDocument129 pagesRay OpticsPriyank Kushwaha100% (2)
- Eye Optics and AccommodationDocument14 pagesEye Optics and AccommodationJúnior AlvesNo ratings yet
- Slit Lamp Bio MicrosDocument21 pagesSlit Lamp Bio MicrosGodwin Ellis67% (3)
- Bifocal & Multifocal: Capt. Dr. Deependra Kumar Sah M.Optom (Bharati Vidyapeeth, Pune) B.Optom (TUTH, IOM)Document66 pagesBifocal & Multifocal: Capt. Dr. Deependra Kumar Sah M.Optom (Bharati Vidyapeeth, Pune) B.Optom (TUTH, IOM)Paudyal IViratNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- Chapter 25 Optical InstrumentsDocument31 pagesChapter 25 Optical InstrumentsJohn Doe100% (1)
- Anatomy of Uvea: Dr. Binu AsharafDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Uvea: Dr. Binu AsharafBinu AshrafNo ratings yet
- CoatingDocument6 pagesCoatingtimi9731No ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World - Notes - 1Document4 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World - Notes - 1Sidra EqbalNo ratings yet
- Optics10 PhysicsDocument10 pagesOptics10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Light-The Human and The Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesLight-The Human and The Colourful WorldTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDocument27 pagesCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0161475410001181 PDFDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0161475410001181 PDFPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Fisio SIO Revisão e Meta Analise 2012 PDFDocument20 pagesFisio SIO Revisão e Meta Analise 2012 PDFMaria Eduarda AlvesNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy in Sport: Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesPhysical Therapy in Sport: Literature ReviewPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy: Eva Barrett, Mary O'Keeffe, Kieran O'Sullivan, Jeremy Lewis, Karen MccreeshDocument9 pagesManual Therapy: Eva Barrett, Mary O'Keeffe, Kieran O'Sullivan, Jeremy Lewis, Karen MccreeshPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy: Chung-Yee Cecilia Ho, Gisela Sole, Joanne MunnDocument12 pagesManual Therapy: Chung-Yee Cecilia Ho, Gisela Sole, Joanne MunnAninda NabilaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Measurement of Posterior Shoulder ExibilityDocument4 pagesClinical Measurement of Posterior Shoulder ExibilityPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Guideline Standards Practice CompleteDocument21 pagesGuideline Standards Practice CompletePrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument2 pagesBudgetPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Safe and Sound Guitar TutorialDocument2 pagesSafe and Sound Guitar TutorialBách NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Soil SSCDocument11 pagesSoil SSCvkjha623477No ratings yet
- API 510 Practise Question Nov 07 Rev1Document200 pagesAPI 510 Practise Question Nov 07 Rev1TRAN THONG SINH100% (3)
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Paper Specific Instructions:: GATE Chemical Engineering MSQ Paper - 1Document11 pagesPaper Specific Instructions:: GATE Chemical Engineering MSQ Paper - 1Mayank ShelarNo ratings yet
- 2005 Harley Davidson Sportster 883 66418Document136 pages2005 Harley Davidson Sportster 883 66418Josef Bruno SchlittenbauerNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 QP PDFDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum 1 QP PDFWai HponeNo ratings yet
- REV Description Appr'D CHK'D Prep'D: Tolerances (Unless Otherwise Stated) - (In)Document2 pagesREV Description Appr'D CHK'D Prep'D: Tolerances (Unless Otherwise Stated) - (In)Bacano CapoeiraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Lab Accidents and PrecautionsDocument6 pagesAssignment - Lab Accidents and PrecautionsAnchu AvinashNo ratings yet
- VPD RashchrtDocument2 pagesVPD RashchrtMarco Ramos JacobNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper-RprDocument6 pagesReaction Paper-Rprapi-543457981No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsHazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Long Term Effects of Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion Without Performing Osteotomy of The Pterygoid PlatesDocument4 pagesLong Term Effects of Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion Without Performing Osteotomy of The Pterygoid PlatesAngélica Valenzuela AndrighiNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts of Enzyme Histochemistry in Modern PathologyDocument11 pagesCurrent Concepts of Enzyme Histochemistry in Modern PathologyRosa AquinoNo ratings yet
- Recruitement Process - Siemens - Sneha Waman Kadam S200030047 PDFDocument7 pagesRecruitement Process - Siemens - Sneha Waman Kadam S200030047 PDFSneha KadamNo ratings yet
- Reading Practice 6Document5 pagesReading Practice 6Âu DươngNo ratings yet
- Parche CRP 65 - Ficha Técnica - en InglesDocument2 pagesParche CRP 65 - Ficha Técnica - en IngleserwinvillarNo ratings yet
- High Speed DoorsDocument64 pagesHigh Speed DoorsVadimMedooffNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Safe Hospital FrameworkDocument12 pagesComprehensive Safe Hospital FrameworkEbby OktaviaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On A Study On Amul Taste of India: Vikash Degree College Sambalpur University, OdishaDocument32 pagesA Project Report On A Study On Amul Taste of India: Vikash Degree College Sambalpur University, OdishaSonu PradhanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Your Questions About Circumcision and HIV/AIDSDocument2 pagesAnswers To Your Questions About Circumcision and HIV/AIDSAlex BrownNo ratings yet
- Gendec - Inbound HS-HTNDocument1 pageGendec - Inbound HS-HTNKhalidNo ratings yet
- PMI Framework Processes PresentationDocument17 pagesPMI Framework Processes PresentationAakash BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Testable HypothesesDocument30 pagesCharacteristics of Testable HypothesesMarivic Diano67% (3)
- Syllabus For Bachelor of Physiotherapy (BPT) Academic ProgrammeDocument36 pagesSyllabus For Bachelor of Physiotherapy (BPT) Academic ProgrammevikasmaeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q4 SML17 V2Document15 pagesScience 9 Q4 SML17 V2HotdogNo ratings yet
- DT 2107Document1 pageDT 2107Richard PeriyanayagamNo ratings yet
- Case Report CMV RetinitisDocument27 pagesCase Report CMV RetinitistaniamaulaniNo ratings yet
- Standards Spec Brochure ME WEBDocument44 pagesStandards Spec Brochure ME WEBReza TambaNo ratings yet