Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Molds and Orthopedic Hardware
Uploaded by
yelbonifacioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Molds and Orthopedic Hardware
Uploaded by
yelbonifacioCopyright:
Available Formats
Casting is a process in which a liquid is poured into a mold in order to produce a product.
There are several types of molds that are used in the casting process. Some are temporary and are destroyed during the casting process.
Others are permanent and are reused again and again.
Sand molds are one of the oldest and most basic types of molds. Dry sand is pressed into a box (called a flask).
A pattern made of wood or metal is pressed into the sand, creating a mold.
Liquid metal or another material can then be poured into the mold, and the excess sand is brushed away when the part has cooled.
Vacuum forming can create many thin, weak molds in a short period of time. A sheet of plastic is suspended over a form, or "buck." The plastic is heated until it is soft, then pressed down on the buck. A vacuum is then turned on beneath the plastic to form it to the shape of the buck. These molds are strong enough to be reused, but thin enough to be cut from the final casting if needed.
Ceramic molds are typically employed with the "lost wax" process of casting. A wax model is created of the desired item. It is then encased in ceramic, leaving a small channel open. When the ceramic is fired the wax melts away, leaving a ceramic mold. The casting material can now be poured in, creating an exact replica of the wax model. When the casting material has hardened, the mold is shattered, freeing the cast.
Permanent molds are often made of steel, iron, silicone or urethane. The casting material is either poured in or injected. Once the cast has hardened, it is removed from the mold. Permanent molds can only be made of hard materials if there are no undercuts in the cast (areas where the cast and the mold lock together). Soft mold materials do not have this issue.
For especially complex castings, multi-piece molds must be used. Often these are two halves that are locked together while the casting is taking place, but molds comprised of many more pieces are used as the casting gets more intricate.
Die casting is the preferred method for creating many small castings. Liquid metal is forced under pressure into a steel mold, or "die." Often many identical castings are built into the same die, allowing rapid manufacture of parts.
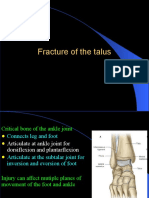
Fracture of Tibia Fibula
Comminuted Fracture for long bonesComminuted Fracture for long bones
Comminuted Fracture: Non healingComminuted Fracture: Non healing
For Post-Op Skin SutureFor Post-Op Skin Suture
For Post- Op DrainageFor Post- Op Drainage
Replacement for infected prothesisReplacement for infected prothesis
Spine
Post- op medication for OsteomyelitisPostop medication for Osteomyeliti
You might also like
- Intramedullary Nailing of The Lower Extremity. Biomechanics and BiologyDocument10 pagesIntramedullary Nailing of The Lower Extremity. Biomechanics and Biologyorthopod_idreesNo ratings yet
- Humeral Shaft Fractures: Nonoperative and Operative Treatment OptionsDocument82 pagesHumeral Shaft Fractures: Nonoperative and Operative Treatment OptionsYoga AninditaNo ratings yet
- 1.26 (Surgery) Orthopedic Pathology - OncologyDocument7 pages1.26 (Surgery) Orthopedic Pathology - OncologyLeo Mari Go LimNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Splints and Tractions GuideDocument26 pagesOrthopedic Splints and Tractions GuideNailahRahmahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 14 - Treatment of Bone Def - 2008 - Surgical Techniques of The ShoulderDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 14 - Treatment of Bone Def - 2008 - Surgical Techniques of The ShoulderJaime Vázquez ZárateNo ratings yet
- Principles in Fracture ManagementDocument60 pagesPrinciples in Fracture ManagementNge NgeNo ratings yet
- DislocationDocument46 pagesDislocationShaa ShawalishaNo ratings yet
- Ortho CompetencesDocument31 pagesOrtho CompetencesHamad ElmoghrabeNo ratings yet
- M.S. Orthopaedic Surgery SyllabusDocument8 pagesM.S. Orthopaedic Surgery SyllabusMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Distal End Humerus Fractures: BY:-Dr. Anshu Sharma Guide:-Dr.A.K. MathurDocument76 pagesDistal End Humerus Fractures: BY:-Dr. Anshu Sharma Guide:-Dr.A.K. MathurToàn Đặng Phan VĩnhNo ratings yet
- Testexam AnswDocument6 pagesTestexam AnswAnaNo ratings yet
- Queens Orthopedic Inpatient Trauma PDFDocument27 pagesQueens Orthopedic Inpatient Trauma PDFRema AmerNo ratings yet
- Acetabular Fracture PostgraduateDocument47 pagesAcetabular Fracture Postgraduatekhalidelsir5100% (1)
- Salter Harris Classification of Growth Plate FracturesDocument13 pagesSalter Harris Classification of Growth Plate FracturesAarón E. CaríasNo ratings yet
- Managing Lumbar Spinal StenosisDocument11 pagesManaging Lumbar Spinal StenosismudassarnatiNo ratings yet
- Modified French OsteotomyDocument5 pagesModified French OsteotomyKaustubh KeskarNo ratings yet
- AdultHip Abstracts PDFDocument106 pagesAdultHip Abstracts PDFJafild Fild riverNo ratings yet
- Club Foot PDFDocument54 pagesClub Foot PDFBelle Sakunrat SarikitNo ratings yet
- Fracture of The Talus and Calcaneus NickDocument43 pagesFracture of The Talus and Calcaneus NickTan Zhi HongNo ratings yet
- Cast and Splint Immobilization - Complications PDFDocument11 pagesCast and Splint Immobilization - Complications PDFcronoss21No ratings yet
- Fractures and Dislocations About The Elbow in The Pediatric PatientDocument65 pagesFractures and Dislocations About The Elbow in The Pediatric PatientPeter HubkaNo ratings yet
- Club Foot-Dr J SahooDocument9 pagesClub Foot-Dr J SahooSheel Gupta100% (1)
- Forearm fracture treatment optionsDocument8 pagesForearm fracture treatment optionsApolinar González HernándezNo ratings yet
- 1.18 (Surgery) General Orthopedics, Open Fractures, Compartment SyndromeDocument5 pages1.18 (Surgery) General Orthopedics, Open Fractures, Compartment SyndromeLeo Mari Go Lim100% (1)
- Endo'S: Surgical TechniqueDocument8 pagesEndo'S: Surgical Techniquefelipefernandezm5105No ratings yet
- Amputation: Sites of Amputation: UEDocument6 pagesAmputation: Sites of Amputation: UEChristine PilarNo ratings yet
- Dr Omer Barawi's guide to diagnosing and treating limb length discrepancyDocument2 pagesDr Omer Barawi's guide to diagnosing and treating limb length discrepancyMuhammed BarznjiNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 Lower Extremity Fracture 2Document22 pagesLect 8 Lower Extremity Fracture 220-221 Crisny Novika Yely Br. HutagaolNo ratings yet
- Avascular NecrosisDocument58 pagesAvascular Necrosischatree100% (4)
- Hip Fractures-Orthoinfo - AaosDocument9 pagesHip Fractures-Orthoinfo - Aaosapi-228773845No ratings yet
- Dislocation: Muhammad ShahiduzzamanDocument30 pagesDislocation: Muhammad ShahiduzzamanAliceNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures With Ilizarov Frame. Maurizio A. Catagni and Francesco GuerreschiDocument4 pagesTreatment of Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures With Ilizarov Frame. Maurizio A. Catagni and Francesco GuerreschiNuno Craveiro LopesNo ratings yet
- Ficat and Arlet staging of hip AVNDocument6 pagesFicat and Arlet staging of hip AVNFernando Sugiarto0% (1)
- David Warwick (Editor), Ashley Blom (Editor), Michael Whitehouse (Editor) - Apley and Solomon - S Concise System of Orthopaedics and Trauma-CRC Press (2022)Document763 pagesDavid Warwick (Editor), Ashley Blom (Editor), Michael Whitehouse (Editor) - Apley and Solomon - S Concise System of Orthopaedics and Trauma-CRC Press (2022)filip100% (1)
- Distal Femur (Sandeep Sir)Document22 pagesDistal Femur (Sandeep Sir)Kirubakaran Saraswathy PattabiramanNo ratings yet
- Tendon TransferDocument1 pageTendon TransferPandi Smart VjNo ratings yet
- Forearm Fractures PDFDocument4 pagesForearm Fractures PDFNur Ashriawati BurhanNo ratings yet
- Why Every Spine Fusion Can Be A Deformity?Document88 pagesWhy Every Spine Fusion Can Be A Deformity?PaulMcAfeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4e Internal MedicineDocument19 pagesChapter 4e Internal MedicinepodmmgfNo ratings yet
- Aaos PDFDocument4 pagesAaos PDFWisnu CahyoNo ratings yet
- Conservative Treatment of Diaphyseal Fractures of Tibia andDocument40 pagesConservative Treatment of Diaphyseal Fractures of Tibia andsaihaNo ratings yet
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocument31 pagesMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesutisuryanjNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide to the General Approach and Management of Orthopedic Trauma and FracturesDocument14 pagesComprehensive Guide to the General Approach and Management of Orthopedic Trauma and FracturesJeffrey Ariesta PutraNo ratings yet
- Gamma NailDocument49 pagesGamma NailMihaela HerghelegiuNo ratings yet
- Approach To FractureDocument17 pagesApproach To FractureRebecca WongNo ratings yet
- Crozer-Keystone Ex Tern Ship ManualDocument187 pagesCrozer-Keystone Ex Tern Ship ManualRihamary CruzNo ratings yet
- Arthroscopic Ankle ArthrodesisDocument37 pagesArthroscopic Ankle ArthrodesisJan VelosoNo ratings yet
- Fracture in ChildrenDocument40 pagesFracture in ChildrenMutiara Jihad100% (1)
- JBLMRH - Ortho - Lag Screw TechniqueDocument17 pagesJBLMRH - Ortho - Lag Screw TechniqueTristan ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Rush Orthopedics Journal 2012Document40 pagesRush Orthopedics Journal 2012rushmedicalNo ratings yet
- Acetabular Fractures: Dr. Roshan DDocument65 pagesAcetabular Fractures: Dr. Roshan DKaizar EnnisNo ratings yet
- Actures - In.adults.8e Booksmedicos - Org Parte4 PDFDocument1 pageActures - In.adults.8e Booksmedicos - Org Parte4 PDFeladioNo ratings yet
- ActuresDocument41 pagesActuressylvester GelacNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Fractures and FixationDocument87 pagesBiomechanics of Fractures and FixationShreya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Osteotomias PediatriaDocument13 pagesOsteotomias PediatriaM Ram CrraNo ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAvascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Current Challenges with their Evolving Solutions in Surgical Practice in West Africa: A ReaderFrom EverandCurrent Challenges with their Evolving Solutions in Surgical Practice in West Africa: A ReaderNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Management in Cerebral Palsy, 2nd EditionFrom EverandOrthopaedic Management in Cerebral Palsy, 2nd EditionHelen Meeks HorstmannRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Mo Slurry Hose Systems - Brochure en 4868 03 23 en MNGDocument27 pagesMo Slurry Hose Systems - Brochure en 4868 03 23 en MNGIgnacio Moratinos CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Applications: by George Schneider, Jr. CmfgeDocument9 pagesCutting Tool Applications: by George Schneider, Jr. CmfgeInfernuzNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Primer Adhesivo Alta Temperatura161916272Document3 pagesFicha Tecnica Primer Adhesivo Alta Temperatura161916272Carlos Tarquino100% (1)
- Vertico SynchroDocument16 pagesVertico SynchrozpramasterNo ratings yet
- Tube Mill Design and Operating ParametersDocument44 pagesTube Mill Design and Operating ParametersRodrigo AlcainoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Building MaterialsDocument12 pagesThermal Properties of Building MaterialsphilipNo ratings yet
- Astm A666 - StainlesssteelDocument8 pagesAstm A666 - StainlesssteelPeter MohabNo ratings yet
- Inspection Report (TRAKINDO)Document2 pagesInspection Report (TRAKINDO)Awang Agus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- MCP101Document9 pagesMCP101Sushant Cr7No ratings yet
- Pipline Cleaning ServicesDocument4 pagesPipline Cleaning Servicesbagus adhitiawarman100% (1)
- Decicoat T35 TDS 703ipDocument3 pagesDecicoat T35 TDS 703ipSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- Pre Painted Coils SpecificationDocument5 pagesPre Painted Coils SpecificationNaveen RohiraNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Prevention Pt2Document33 pagesCorrosion Prevention Pt2allanNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet for High-Performance Epoxy CoatingDocument5 pagesTechnical Data Sheet for High-Performance Epoxy CoatingDamar WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Paperppt 170831195446Document27 pagesPaperppt 170831195446vankayalasuryaNo ratings yet
- Filter Element OverviewDocument6 pagesFilter Element Overviewmona zhangNo ratings yet
- Az 5214eDocument3 pagesAz 5214ekisupNo ratings yet
- Novaporte StiffDocument6 pagesNovaporte StiffBenoit DumonteilNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Glossary DefinitionsDocument88 pagesPulp and Paper Glossary Definitionsandhie68No ratings yet
- Plastic Welding TechniquesDocument33 pagesPlastic Welding TechniquesFaiz SabianNo ratings yet
- TR2000 - Get Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageTR2000 - Get Datasheet PDFwendeltrentoNo ratings yet
- Polyester 20 Resin 20 FinalDocument5 pagesPolyester 20 Resin 20 FinalZdravko GrbićNo ratings yet
- En GJL 250Document2 pagesEn GJL 250StefanoDelTedescoNo ratings yet
- Forging PDFDocument16 pagesForging PDFloveguru2512No ratings yet
- Aeration Industries International, Inc. Aire-O Microfloat DAF Case StudyDocument6 pagesAeration Industries International, Inc. Aire-O Microfloat DAF Case StudyDileep C DileepNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection Consumables PDFDocument28 pagesWelding Inspection Consumables PDFJoseph PeterNo ratings yet
- 8 Welding SymbolsDocument43 pages8 Welding Symbolsjamilhse7759No ratings yet
- Endura Stone Installation InstructionsDocument8 pagesEndura Stone Installation InstructionsSeif EddineNo ratings yet
- Industrial Arts 6: Week 1Document12 pagesIndustrial Arts 6: Week 1JIAN M. PURUNTONG100% (1)
- Economic and Product Design Considerations in Machiningchapter 24Document38 pagesEconomic and Product Design Considerations in Machiningchapter 24احمد عمر حديدNo ratings yet