Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethics Theories of Ethics: Instructor - Dr. Sikharini Majumdar Course - 206, Room No. 309
Uploaded by
Abhishek ChakrabortyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethics Theories of Ethics: Instructor - Dr. Sikharini Majumdar Course - 206, Room No. 309
Uploaded by
Abhishek ChakrabortyCopyright:
Available Formats
ETHICS THEORIES OF ETHICS Instructor - Dr. Sikharini Majumdar Course 206, Room No.
309
Information
Class MHRM, 4th semester Location Room No. 309, Management House, IISWBM Schedule
Book(s)
Required Text Additional
Item 1 Item 2 Item 3
Materials
Tuesday 12 noon 1:30 p.m. Lab Tues-Thurs
Office Phone 319 Email meghpeon@gmail.com
Introduction to Ethics
The word ethics comes from the Greek ethos, meaning something like morals. In fact, ethics is defined as the systematic reflection on what is moral. In this definition, morality is the whole of opinions, decisions and actions with which people express what they think is good or right.
Introduction to ETHICS:
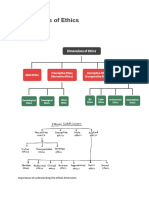
We can identify two kinds of Ethics: The descriptive ethics is involved with the description of existing morality. It is about facts. Descriptive judgments are therefore true or false. The prescriptive ethics is also known as the normative ethics. This branch of ethics actually judges morality. Normative judgments are therefore value judgments: they indicate whether something is good or bad.
Normative Ethics
Normative Relativism - states that all moral points of view are relative. (1) The morals of one person are not necessarily equal to the morals of another person. (2) Certain norms and values are better than other norms and values is also not acceptable. The problem with this theory is that it allows all norms and values.
Absolutism
On the other hand is absolutism, also known as universalism. It states that there is a system of norms and values that is universally applicable to everyone, everywhere at every time. Absolutism makes no exceptions: a rule is a rule. However, there is no set of norms and values that never contradicts itself. So, absolutism in general doesnt work.
Classical Theory
Socrates, the patron saint of moral philosophy: We ought never to harm anyone, We ought to keep our promises We ought to respect our parents and teachers The central theme in virtue ethics is shaping people into morally good and responsible creatures influenced by Aristotle.
Deontological maintains that the basic judgment of obligation or duty are purely particular (e.g. - Kant)
Teleological result of the deed (happiness, pleasure as opposed to pain, sadness).
Kantian Theory
Immanuel Kant has developed the most well known system of duty ethics: the Kantian theory. A core notion here is autonomy. A man should place a moral norm upon himself and obey it. This is his duty. He should then, on his own, be able to determine through reasoning what is morally correct.
Kantian Theory
The Kantian theory is part of monistic duty ethics: Universality principle: Act only on that maxim which you can at the same time will that it should become a universal law. Reciprocity principle: Act as to treat humanity, whether in your own person or in that of any other, in every case as an end, never as means only.
Negativity of Kantian Theory of Ethics
In Kants theory, rules can not be bent. This reminds us of absolutism. So, the question arises whether all the moral laws form a consistent system of norms. Another downside is that Kantian theory prescribes to rigidly adhere to the rules, irrespective of the consequences. But in real life, following a rule can of course have very negative consequences. Kants theory does not deal with these exceptions.
Utilitarianism
Promotes greatest good of the greatest number (John Stuart Mill, teleological) The principle of utility is the ultimate standard It is to be appealed to at the level of rules rather than at the level of particular judgments. Ethical egoism one is always to do what will promote his own greatest good (Hobbes, Nietzsche)
Social Justice: Equality
Distributive justice Treating people equally (may not be identically) Does not mean making lives equally good or maintaining their lives at the same level of goodness Ethics of Love (Judeo-Christian) Utilitarian theology (John Locke)
Questions/Discussions
Question One
Discussion Discussion
Question Two
Discussion Discussion
Questions Three
You might also like
- WFRP Salzenmund 20220617v2-141Document1 pageWFRP Salzenmund 20220617v2-141Rakdos OrthvetNo ratings yet
- Soft Skills PDFDocument117 pagesSoft Skills PDFAditia Darmadi J.No ratings yet
- Ethical TheoriesDocument3 pagesEthical TheoriesAlbert MukiriaNo ratings yet
- TRUST Deed Model Draft Sample With Extracts of Minutes of MeetingDocument12 pagesTRUST Deed Model Draft Sample With Extracts of Minutes of MeetingvishchandraNo ratings yet
- Ethical FrameworkDocument5 pagesEthical FrameworkJean Ester Evangelio CortejoNo ratings yet
- Recruitment QuestionnaireDocument10 pagesRecruitment QuestionnaireGnanaganesan74% (34)
- AxiologyDocument30 pagesAxiologySh. Khurram AbidNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture and SocietyDocument39 pagesUnderstanding Culture and SocietyReyna RodelasNo ratings yet
- Ethics Book Values and VirtuesDocument237 pagesEthics Book Values and Virtuessarang11100% (1)
- What Is EthicsDocument12 pagesWhat Is EthicsLauraNo ratings yet
- Ethical Theories and Decision MakingDocument32 pagesEthical Theories and Decision Makingmuwonge mosesNo ratings yet
- Frameworks and Principles Behind Our Moral DispositionsDocument29 pagesFrameworks and Principles Behind Our Moral DispositionsKlim Hazel Racal Lumansoc100% (7)
- Theory of Practie of Counseling and PsuchotheraphyDocument22 pagesTheory of Practie of Counseling and PsuchotheraphyMohd Shahlan Sidi Ahmad100% (6)
- Ineng Vs Vega AmoriioDocument3 pagesIneng Vs Vega AmoriioPaolo PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Unit I. Theories and Principles of Health EthicsDocument6 pagesUnit I. Theories and Principles of Health EthicsShane PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Ethical FrameworkDocument11 pagesEthical Frameworkdanish_1985No ratings yet
- ETHICS REVIEWER WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesETHICS REVIEWER WPS OfficeClare LuzonNo ratings yet
- Making Choices: A Framework For Making Ethical DecisionsDocument12 pagesMaking Choices: A Framework For Making Ethical DecisionsDennis NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Ethics and moral theoriesDocument4 pagesEthics and moral theoriesPatrick AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- MBA Ethical Theories Guide: Normative, Descriptive, Meta EthicsDocument47 pagesMBA Ethical Theories Guide: Normative, Descriptive, Meta EthicsPushpendra SinghNo ratings yet
- p1 EthicsDocument4 pagesp1 EthicsJohn Aldrin Santiago PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Application to Business Ethics/TITLEDocument25 pagesApplication to Business Ethics/TITLEAnup PaulNo ratings yet
- Global Ethics Week 6 Summary Lecture 1 2024Document83 pagesGlobal Ethics Week 6 Summary Lecture 1 2024zhengsiyuan26No ratings yet
- Reviewer For Finals EthicsDocument3 pagesReviewer For Finals EthicsChelsei Jometh D. AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Absolute vs relative moralityDocument3 pagesAbsolute vs relative moralityrtrtrt6No ratings yet
- Cyber NotesDocument61 pagesCyber NotesEmma mutaurwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ethics and Values in 26Document5 pagesChapter 3 Ethics and Values in 26Mallesh ViruNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics TheoriesDocument50 pagesBusiness Ethics TheoriesVarun VigneshNo ratings yet
- Three Major Theories Of EthicsDocument3 pagesThree Major Theories Of EthicsAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document22 pagesChapter 7harshadampgdmNo ratings yet
- Ethical TheoriesDocument8 pagesEthical Theoriesمنذر رضاNo ratings yet
- M1 LT4 Aguado 21Document4 pagesM1 LT4 Aguado 21EMMANo ratings yet
- Dimensions of EthicsDocument13 pagesDimensions of EthicsPravesh Kumar KohliNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument4 pagesEthicsJRNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS ETHICS:: Kantian Ethics (Deontology) : Metaphysics of Morals (1785), Critique of Practical Reason (1788) andDocument4 pagesBUSINESS ETHICS:: Kantian Ethics (Deontology) : Metaphysics of Morals (1785), Critique of Practical Reason (1788) andRanger KnightsNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Overview of EthicsDocument5 pagesModule 2 - Overview of EthicsWilmarie Hope Aliling100% (1)
- Ethics and Theories of EthicsDocument35 pagesEthics and Theories of Ethicsashenafi chekolNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ethics: IT104-Lesson 1Document31 pagesIntroduction To Ethics: IT104-Lesson 1Denver Iñigo PartibleNo ratings yet
- Ch03-Ethics and Ethical AnalysisDocument25 pagesCh03-Ethics and Ethical AnalysisEng. Abdullahi NuxurNo ratings yet
- Business Applications of Ethical TheoriesDocument27 pagesBusiness Applications of Ethical TheoriescrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- Philo Finals Oral ExamDocument9 pagesPhilo Finals Oral ExamMary Margareth GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ETHICS THEORIES UNDER 40Document10 pagesETHICS THEORIES UNDER 40calvinNo ratings yet
- Midterm GE 2 Ethics Week 11 Module 9Document7 pagesMidterm GE 2 Ethics Week 11 Module 9Jhon Mark RabeNo ratings yet
- Consequentialism Consequences of An Action Are The Basis For Valid JudgmentsDocument6 pagesConsequentialism Consequences of An Action Are The Basis For Valid JudgmentsAndy HouNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Morality & TheoryDocument48 pagesBioethics Morality & TheoryBarbara Gatumuta100% (1)
- Normative Ethics 1: Ethics or Moral Philosophy Is The Study of Codes of Conduct That Govern Our BehaviourDocument28 pagesNormative Ethics 1: Ethics or Moral Philosophy Is The Study of Codes of Conduct That Govern Our BehaviourЕкатерина КрыловаNo ratings yet
- Topics Handout 1Document10 pagesTopics Handout 1calvinNo ratings yet
- Basha Civics Chapter 2Document20 pagesBasha Civics Chapter 2nebiyat tadiwosNo ratings yet
- DMK - Module8 GE8 ETHDocument10 pagesDMK - Module8 GE8 ETHJINKY TOLENTINONo ratings yet
- Civics Chapter2Document17 pagesCivics Chapter2Sara MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four - Ethical TheoriesDocument23 pagesChapter Four - Ethical TheoriesStar branchNo ratings yet
- Ethics Ma'am OrugaDocument13 pagesEthics Ma'am OrugaItachi03No ratings yet
- WK 2 - Introduction To EthicsDocument32 pagesWK 2 - Introduction To EthicsHanz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Moral Theories Research PaperDocument7 pagesMoral Theories Research PaperKortnie GibsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two NotesDocument8 pagesChapter Two NotesHanan FuadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document17 pagesChapter 9MahmoudKhedrNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument6 pagesEthicsSakub Amin Sick'L'No ratings yet
- Ethics Theories and Concepts ExplainedDocument26 pagesEthics Theories and Concepts ExplainedTesfayé HailuNo ratings yet
- Ethics FLMS Activity 8Document2 pagesEthics FLMS Activity 8maryie lapecerosNo ratings yet
- Kantian Ethics: Categorical ImperativeDocument4 pagesKantian Ethics: Categorical ImperativeMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- CSR Ananya Gaba 010Document29 pagesCSR Ananya Gaba 010Ashish SarohNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Nature of EthicsDocument17 pagesModule 1-Nature of EthicsClarisse Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- AsiaSweep 2013 AnswersDocument352 pagesAsiaSweep 2013 AnswersAbhishek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Sap MM NotesDocument17 pagesSap MM Notesaisha4u123No ratings yet
- 95 Excel Tipsv 4Document28 pages95 Excel Tipsv 4namrattaNo ratings yet
- ICICI Business Leadership ProgrammeDocument3 pagesICICI Business Leadership ProgrammeAbhishek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Sap MM NotesDocument17 pagesSap MM Notesaisha4u123No ratings yet
- Wage DeterminationDocument35 pagesWage DeterminationAbhishek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Document SummaryDocument126 pagesRoad Safety Document SummaryAbhishek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Six Thinking HatsDocument15 pagesSix Thinking HatsFlora Elena SandovalNo ratings yet
- 2002 329 033 ReadingDocument7 pages2002 329 033 ReadingAbhishek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Leader and MangerDocument1 pageDifference Between Leader and MangerAbhishek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- A Letter From The YouthDocument3 pagesA Letter From The YouthIyra Celis-CastilloNo ratings yet
- Anti & Alter GlobalizationDocument11 pagesAnti & Alter GlobalizationJahedHossainNo ratings yet
- Law on Public OfficersDocument27 pagesLaw on Public OfficersMarvin CabantacNo ratings yet
- BPI V. DE COSTER: Agent Cannot Make Principal Liable for Third Party DebtsDocument2 pagesBPI V. DE COSTER: Agent Cannot Make Principal Liable for Third Party DebtsTonifranz Sareno100% (1)
- JUTA's StatementDocument1 pageJUTA's StatementThe WireNo ratings yet
- Understanding THE: F.L. Vargas College SY 2019-2020Document26 pagesUnderstanding THE: F.L. Vargas College SY 2019-2020Ikaw Lang Onalac100% (1)
- Inductive & Deductive ReasoningDocument12 pagesInductive & Deductive ReasoningKirti Rai ChanchalNo ratings yet
- Organization Associated With Biodiversity Organization-Methodology For Execution IucnDocument45 pagesOrganization Associated With Biodiversity Organization-Methodology For Execution IucnmithunTNNo ratings yet
- Negotiation: Section 01: Negotiation Fundamentals The Nature of NegotiationDocument16 pagesNegotiation: Section 01: Negotiation Fundamentals The Nature of NegotiationAkshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Ethics and ResponsibilitiesDocument19 pagesCivil Engineering Ethics and ResponsibilitiesNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Part 3Document14 pagesModule 1 Part 3mohithpola21No ratings yet
- Omnibus Order On MSJ, Officer Alfred Stabile, City of Hollywood Police DepartmentDocument11 pagesOmnibus Order On MSJ, Officer Alfred Stabile, City of Hollywood Police Departmentdj149527100% (1)
- APA Pilots Legal Rights After Airline RestructureDocument7 pagesAPA Pilots Legal Rights After Airline RestructureDaniel Goh100% (1)
- Songs of Light and Prayer from Around the WorldDocument438 pagesSongs of Light and Prayer from Around the WorldHari Baldo0% (1)
- Preconceito RacialDocument3 pagesPreconceito RacialJanaina FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Sample MemorialDocument26 pagesSample MemorialShr33% (3)
- Investment Law Projec - SANDESHNIRANJANDocument22 pagesInvestment Law Projec - SANDESHNIRANJANSandeshNiranjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Organizational Ethics and The Law: Answer KeyDocument6 pagesChapter 05 Organizational Ethics and The Law: Answer KeyMaryam Al-Samhan100% (1)
- Cui V Cui 1957Document3 pagesCui V Cui 1957Angelette BulacanNo ratings yet
- Sihi V IacDocument2 pagesSihi V IacFrancis Kyle Cagalingan SubidoNo ratings yet
- 02 McGuigan CH 01Document14 pages02 McGuigan CH 01Zoran BosevskiNo ratings yet
- Quality ImprovementDocument49 pagesQuality ImprovementritaanggraeniNo ratings yet
- 61 Maquera V BorraDocument2 pages61 Maquera V BorraCarie LawyerrNo ratings yet