Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dye Lasers: Large Size Organic Molecules
Uploaded by
Jay TiwariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dye Lasers: Large Size Organic Molecules
Uploaded by
Jay TiwariCopyright:
Available Formats
Dye lasers
Large size organic molecules
Dye solutions/dyes doped in solid matrix (polymers / organic molecules) Liquid lasers/dye doped solid state lasers
Typical dyes
Energy levels
Energy levels (simplified model)
Dye absorption
Absorption and emission
Dye emission
Green dye absorption Yellow dye emission
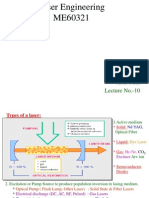
Pumps 1. Flash lamp 2. Lasers( N2, excimer, Nd, ion lasers, Cu vapour etc) Pulsed systems/ CW systems Photo-degradation; dye degrades on absorption of light; limits the life of the dye Continuous circulation for CW lasers
Flash lamp pumped dye laser
Linear/coaxial flash lamp pumped laser, dye solution is made to flow; in low power dye circulation is under gravity while high power sources it is pumps are used Average power ~ several KW Pulse energy ~ 100J/10Hz UV-IR, 1GHz line-width 1-5000s pulse widths, 1ps pulses have been produced 1-2% wall-plug efficiency
Schematics of a flash lamp pumped dye laser
Laser output of flash lamp dye lasers Linear/coaxial flash lamp pumped laser, dye solution is made to flow; in low power dye circulation is under gravity while high power sources it is pumps are used Average power ~ several KW Pulse energy ~ 100J/10Hz UV-IR, 1GHz line-width 1-5000s pulse widths, 1ps pulses have been produced 1-2% wall-plug efficiency
Typical pulsed laser pumped dye laser
Tuning element
Schematics of a laser pumped pulsed dye laser
Tuning element
With magnetic stirrer
N2 laser pumped dye laser
OUTPUT CYLINDRICAL LENS N2 LASER DYE CELL
N2 laser pumped dye laser; ANNIMATION
Schematics of laser pumped CW dye laser (linear cavity)
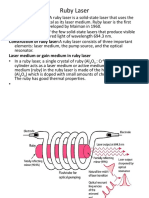
Dye doped solid state lasers
Rd6G doped LAP developed at IIT Kanpur
PMMA,MPG (polymers), silicate glass, phosphate glass, silica gel etc available commercially
Q-switching Quality factor Q of a resonator is the measure of the amount of energy that can be stored in the resonator. A high Q factor corresponds to low resonator losses per roundtrip, and vice versa. Q=- /(d/dt), where is the stored energy; in case of a laser resonator energy is stored in the form of population inversion density. Q=/ ( 1/2) In lasers we have Q-switching; a
Q-switching (Contd) Initially the laser medium is pumped while the Q-switch prevents feedback of light into the gain medium (producing an optical resonator with low Q). This produces a population inversion, but laser operation cannot yet occur since there is no feedback from the resonator. Since the rate of stimulated emission is dependent on the amount of light entering the medium, the amount of energy stored in the gain medium increases as the medium is pumped. Due to losses from spontaneous emission and other processes, after a certain time the stored energy will reach some maximum level; the medium is said to be gain saturated. At this point, the Q-switch device is quickly changed from low to high Q, allowing feedback and the process of optical amplification by stimulated emission to begin. Because of the large amount of energy already stored in the gain medium, the intensity of light in the laser resonator builds up very quickly; this also causes the energy stored in the medium to be depleted almost
Q-switching techniques 1. Mechanical methods a.Rotating resonator mirror
b. Mechanical chopper inside laser cavity
Q-switching techniques (contd.) Saturable absorber (absorption changes with intensity)
Q-switching techniques (contd.) Electro-optic/magneto-optic/acoustooptic switches Refractive index is modulated by application of voltage / acoustic wave
Acousto-optic Q-switch
Electro-optic Q-switch Polarization is changed on application of voltage, so the laser cavity has high loss(low Q). Suddenly voltage is switched-off and Q of cavity is high and a laser output in the form of pulse is observed
Q-switching increases peak power. What about the average power? Does it also increase? Think
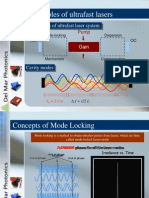
Mode-locking Output of a windows
Output of a laser Out-put of a laser which has with Brewster cylindrical windows The output is viewed in asymmetry plan
perpendicular to laser-axis (line joining the resonator mirrors through the gain medium); transverse laser modes
You might also like
- Important - Laser and Q SwitchDocument49 pagesImportant - Laser and Q SwitchAyush GhoshNo ratings yet
- PDF 13jan24 0815 SplittedDocument6 pagesPDF 13jan24 0815 Splittedrokesh123ee3No ratings yet
- 15-Laser Techniques QswitchingDocument15 pages15-Laser Techniques QswitchingAshish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Laser by Abhi DokanDocument27 pagesLaser by Abhi DokanAbhishek DokanNo ratings yet
- 10 Q - Switching & Mode LockingDocument21 pages10 Q - Switching & Mode Lockingkaushik42080% (1)
- High Power LASERDocument22 pagesHigh Power LASERVIJEESH PNo ratings yet
- Liquid and Dye LaserDocument12 pagesLiquid and Dye LaserKumar AshishNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument38 pagesLaserBengüsu GüvenNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam MachiningDocument37 pagesLaser Beam MachiningramuNo ratings yet
- Laser Module 1Document24 pagesLaser Module 1Luis Enrique B GNo ratings yet
- NTMP 2&3Document22 pagesNTMP 2&3Nishant PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Optically Pumped Laser GuideDocument6 pagesOptically Pumped Laser GuidegitaNo ratings yet
- Photo Detectors PDFDocument80 pagesPhoto Detectors PDFdevendrakphyNo ratings yet
- Solid State Lasers and Applns - RKDocument56 pagesSolid State Lasers and Applns - RKAbhishek KumbalurNo ratings yet
- LASER Basics and Q-Switching Techniques ExplainedDocument12 pagesLASER Basics and Q-Switching Techniques ExplainedZaffu ZealyNo ratings yet
- COURSEPAGE DUMP - BMD407 LASERS AND FIBEROPTICS IN MEDICINE - Types of LaserDocument24 pagesCOURSEPAGE DUMP - BMD407 LASERS AND FIBEROPTICS IN MEDICINE - Types of LaserSuvankar ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Laser Types: According To The Wavelength: Infra-Red, Visible, Ultra-Violet (UV) or X-Ray LasersDocument23 pagesLaser Types: According To The Wavelength: Infra-Red, Visible, Ultra-Violet (UV) or X-Ray LasersTitus Samuel SudandararajNo ratings yet
- 10B1NPH831 PhotonicsDocument29 pages10B1NPH831 Photonicsneha gargNo ratings yet
- Lect9 Laser OscillatorsDocument91 pagesLect9 Laser OscillatorsEligius MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ight Mplification by Timulated Mission of Adiation: L A S E RDocument40 pagesIght Mplification by Timulated Mission of Adiation: L A S E RSparsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Helium - Neon Laser: Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument7 pagesHelium - Neon Laser: Optical Fiber CommunicationHafiz Hassan Hyder Khan LodhiNo ratings yet
- ND: YAG Laser (Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) : (J. E. Geusic Et Al. at Bell Laboratories in 1964)Document35 pagesND: YAG Laser (Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) : (J. E. Geusic Et Al. at Bell Laboratories in 1964)Armaan MalikNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Passively Q-Switched Lasers: DegnanDocument12 pagesOptimization of Passively Q-Switched Lasers: DegnanRay JonesNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument17 pagesPhysics NotesAdarsh MenonNo ratings yet
- Sources Plus DetectorsDocument19 pagesSources Plus DetectorsHussain BarwahwalaNo ratings yet
- Laser Pumping MechanismDocument69 pagesLaser Pumping MechanismRajas Khokle80% (5)
- Optical Sources DetectorsDocument72 pagesOptical Sources DetectorsDivyank BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Assign 4175Document8 pagesAssign 4175Md pacificNo ratings yet
- IV. Laser Diode (LD) or Semiconductor LaserDocument27 pagesIV. Laser Diode (LD) or Semiconductor LaserSagar BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 01 Renk - Basics of Laser Physics For Students of Science and Engineering-235-244Document10 pages01 Renk - Basics of Laser Physics For Students of Science and Engineering-235-244LuisaSánchezNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument28 pagesLaserHARSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Laser Engineering ME60321 Lecture No.-10 Types Excitation Sources Population Inversion LasersDocument28 pagesLaser Engineering ME60321 Lecture No.-10 Types Excitation Sources Population Inversion LaserszxcvuiopNo ratings yet
- Solid State Laser Pumping For Non Linear Frequency ConversionDocument12 pagesSolid State Laser Pumping For Non Linear Frequency ConversionsankariNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument14 pagesLasersjerry cristianoNo ratings yet
- Dye LasersDocument11 pagesDye LasersMousumiNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Light Dependent Resistors (LDRsDocument18 pagesThe Complete Guide to Light Dependent Resistors (LDRsjrajaNo ratings yet
- Ir Trans and ReceiverDocument13 pagesIr Trans and ReceiverAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Laser EngineeringDocument19 pagesLecture 17 - Laser EngineeringGaurav GodseNo ratings yet
- Coupled-Cavity Resonant Passive Mode-Locked Nd:yttrium Lithium Fluoride LaserDocument3 pagesCoupled-Cavity Resonant Passive Mode-Locked Nd:yttrium Lithium Fluoride LaserLaura ZahariaNo ratings yet
- Co 2 LaserDocument9 pagesCo 2 LaserAli VatanNo ratings yet
- 03laser Construction (English)Document11 pages03laser Construction (English)Adarsh SmgNo ratings yet
- Scalable Concept For Diode-Pumped High-Power Solid-State LasersDocument8 pagesScalable Concept For Diode-Pumped High-Power Solid-State LasersshiwwasujiNo ratings yet
- Some Basics of LasersDocument102 pagesSome Basics of LasersVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Optical Detector - RBDocument49 pagesOptical Detector - RBK. ogareNo ratings yet
- FPI Laser Wavelength MeasurementDocument26 pagesFPI Laser Wavelength MeasurementAkon HolmesNo ratings yet
- Winter College on Optics: Trends in Laser Development and Multidisciplinary ApplicationsDocument34 pagesWinter College on Optics: Trends in Laser Development and Multidisciplinary ApplicationsPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On LaserDocument19 pagesPresentation On LaserBhargavNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument173 pagesLasersCompengtech DeptNo ratings yet
- Acronym Visible Light Maser Radio Frequencies Bell Telephone LaboratoriesDocument6 pagesAcronym Visible Light Maser Radio Frequencies Bell Telephone LaboratoriesMahendran MaheNo ratings yet
- Ruby and He-NeDocument18 pagesRuby and He-NeEhs AanNo ratings yet
- Spectral Matching of LEDs and Photoconductive CellsDocument5 pagesSpectral Matching of LEDs and Photoconductive CellsattapapaNo ratings yet
- L18 Sources IIIDocument19 pagesL18 Sources IIIsvedika18No ratings yet
- Controlling Laser Power with Acousto-Optic Modulators (AOMsDocument4 pagesControlling Laser Power with Acousto-Optic Modulators (AOMsJashan BansalNo ratings yet
- Application Notes-Photoconductive Cells: Application Note #1 Light - Some Physical BasicsDocument5 pagesApplication Notes-Photoconductive Cells: Application Note #1 Light - Some Physical Basicsjagm2000No ratings yet
- Laser in STEM Jagadish-1Document6 pagesLaser in STEM Jagadish-1jagadish rottyNo ratings yet
- Lasers: Ight Mplification by Timulated Mission AdiationDocument34 pagesLasers: Ight Mplification by Timulated Mission AdiationkaneeshaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Types of Lasers: Lasers May Be Classified According To Several CriteriaDocument8 pages1.5 Types of Lasers: Lasers May Be Classified According To Several CriteriaCătălin Tenchiu100% (1)
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- ds12887 RTC InterfacingDocument11 pagesds12887 RTC InterfacingJay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hall BookDocument126 pagesHall BookbanguyenbkNo ratings yet
- 8051 Addressing ModesDocument15 pages8051 Addressing ModesJay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lmece 303and Ece353 Latest - New 1-1Document36 pagesLmece 303and Ece353 Latest - New 1-1Jay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Tughlaq7-9Document6 pagesTughlaq7-9Jay TiwariNo ratings yet
- 2 - Managerial Functions & SkillsDocument15 pages2 - Managerial Functions & SkillsJay Tiwari100% (1)
- Fractional Laser: Santi Devina Pembimbing: Dr. Lynda Hariani, Sp. Bp-Re Textbook Reading 12 Februari 2016Document27 pagesFractional Laser: Santi Devina Pembimbing: Dr. Lynda Hariani, Sp. Bp-Re Textbook Reading 12 Februari 2016Habibie AinunNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument20 pagesSeminarGaurav UmarNo ratings yet
- Laser Principles: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimDocument13 pagesLaser Principles: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimjohnNo ratings yet
- Gas Laser PDFDocument3 pagesGas Laser PDFIbrahimo BanzeNo ratings yet
- Laser - WikipediaDocument25 pagesLaser - WikipediaSementaraSementaraNo ratings yet
- He-Ne LaserDocument15 pagesHe-Ne Laserritik gargNo ratings yet
- Laser-Hybrid WeldingDocument2 pagesLaser-Hybrid WeldingVysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet
- UNIT V - Applied Optics - LASER Physics MCQDocument2 pagesUNIT V - Applied Optics - LASER Physics MCQsiva kesavNo ratings yet
- Lasers and Their Many UsesDocument27 pagesLasers and Their Many UsesnawidNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Frequency Chirping of Semiconductor Lasers in The Presence of Optical FeedbackDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Frequency Chirping of Semiconductor Lasers in The Presence of Optical FeedbackRIzwanaNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument29 pagesLasersasadNo ratings yet
- Historylasers PDFDocument8 pagesHistorylasers PDFGwen WalkerNo ratings yet
- Ruby Laser and CO2 Laser - PowerPointToPdfDocument15 pagesRuby Laser and CO2 Laser - PowerPointToPdfchirag pandeyNo ratings yet
- Lumenis - M22 - Before and After Case Book PDFDocument28 pagesLumenis - M22 - Before and After Case Book PDFPatrick Kim100% (1)
- Laser Term PaperDocument9 pagesLaser Term PaperSudhanshu SekharNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting Machine Main Accessories Price ListDocument1 pageLaser Cutting Machine Main Accessories Price Listjaiveer.comNo ratings yet
- Fiber Laser Cleaning Machine - Intouch GroupDocument15 pagesFiber Laser Cleaning Machine - Intouch GroupClaudio Duran CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Linscan Resultados 1Document6 pagesLinscan Resultados 1ASRAXNo ratings yet
- Laser Ignition SystemDocument13 pagesLaser Ignition SystemPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- CrystalDocument23 pagesCrystalTema HassanNo ratings yet
- Coupled-Cavity Resonant Passive Mode-Locked Nd:yttrium Lithium Fluoride LaserDocument3 pagesCoupled-Cavity Resonant Passive Mode-Locked Nd:yttrium Lithium Fluoride LaserLaura ZahariaNo ratings yet
- A Ruby Laser Is A SolidDocument2 pagesA Ruby Laser Is A SolidDevid gakharNo ratings yet
- Monolithic Fiber Laser Oscillator With Record HighDocument7 pagesMonolithic Fiber Laser Oscillator With Record Highali2296No ratings yet
- Diode-Pumped Tm:YAG Microchip LaserDocument79 pagesDiode-Pumped Tm:YAG Microchip Lasers rNo ratings yet
- Femtosecond Laser PDFDocument2 pagesFemtosecond Laser PDFVirginiaNo ratings yet
- Nabeel 221370204Document14 pagesNabeel 221370204Nabeel NazeerNo ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology: 15U002 Fibre Optics and Laser InstrumentsDocument22 pagesPSG College of Technology: 15U002 Fibre Optics and Laser InstrumentsDharshan kumarNo ratings yet
- ND LaserDocument1 pageND Lasertayyabi@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1K Ismail JabiullaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - SMC Bulletin AprilDocument64 pages2017 - SMC Bulletin AprilMaurya GyanprakashNo ratings yet