Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human's Sense Organs
Uploaded by
Tiara CalistaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human's Sense Organs
Uploaded by
Tiara CalistaCopyright:
Available Formats
Humans Sense Organs
Tiara Calista IX-1 / 19 State Junior High School 1 Sidoarjo
Light eyes afferent neurone brain efferent neurone effector response
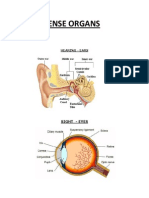
Part of Eye Cornea
Function / Definition
a tough, five-layered membrane through which light is admitted to the interior of the eye. the colorful part of the eye, control how much light Iris goes through the pupil. black circle in the center of the iris, and it lets light Pupil enter the eye. Anterior Chamber the space between the cornea and the iris, contains transparent fluids that nourishes the eye. Lens focus light rays on the back of the eyeball (retina) Retina Rod nerve cells (inside retina) Cone nerve cells (inside retina) takes the light received by the eye and changes it into nerve signals, then send those signals to brain. see in black, white, and shades of gray and tell us the form or shape that something has. sense color and they need more light than rods to work well.
Sound ears afferent neurone brain efferent neurone effector response
Part of Ear Outer Ear
Function / Definition visible portion of the ear, which serves as a protective organ for the eardrum. It collects and guides the sound waves into the middle ear. vibrates as soon as it receives the sound waves and transforms the sound energy into the mechanical energy.
Eardrum (tympanic membrane)
Malleus, Incus, receive vibration from eardrum and tansmit to inner Stapes ear. Cochlea Semicircular Canals the membrane lining of cochlea consists of numerous nerve cells. These are fluid-filled loops, attached to the cochlea and helps in maintaining the balance.
Auditory Nerve The electrical impulses, generated by the nerve cells, are then passed to the brain.
Touch skin afferent neurone brain efferent neurone effector response
Part of Skin Hair Sweat Gland Oil Gland Epidermis
Function / Definition keep the body warm by trapping air underneath them. regulate bodys temperature produce an oily secretion, called sebum, which is skin's natural lubricant. protects the body from invasion and infection and helps to seal in moisture.
Dermis
Fat layer
consists of bundles of tough fibers which give the skin its elasticity, firmness and strength. There are also blood vessels, which feed vital nutrients to these areas Attaches the skin to internal organs
Odor nose afferent neurone brain efferent neurone effector response
Part of Nose Nostril
Function / Definition one of two openings to the nose.
Nasal Bone
Olfactory nerve
two oblong shaped bones which connect vertically and run from the top to the middle of the nose. They form the bridge of the nose and vary in size depending on the individual. transmits the sense of smell from the nasal cavity to the brain.
Chemical tongue afferent neurone brain efferent neurone effector response
Part of Nose Papillae
Function / Definition contains taste bud (chemo-receptors), which helps us identify between different tastes of food. Helps in filtering germs secures or holds the tongue in place inside the mouth
Tonsils Frenulum linguae
You might also like
- Yuzuru Hanyu - ThesisDocument6 pagesYuzuru Hanyu - ThesisFatima Esperanza Ortiz Ortiz100% (4)
- Laboratory Work 1 Computation of Metrics of Productivity of Computer SystemDocument12 pagesLaboratory Work 1 Computation of Metrics of Productivity of Computer SystemHhhhhh75% (4)
- Western Dragon V3 Updated PDFDocument19 pagesWestern Dragon V3 Updated PDFMark Moldez94% (17)
- EcholocationDocument14 pagesEcholocationapi-238216496No ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Document2 pagesCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Palak SinghDocument19 pagesPalak SinghPalak Singh0% (1)
- Lab 6 PDFDocument6 pagesLab 6 PDFSamuel AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Fascial Manipulation For Internal Dysfunctions FMIDDocument8 pagesFascial Manipulation For Internal Dysfunctions FMIDdavidzhouNo ratings yet
- 20 - Low-Cycle Fatigue of Turbocharger Compressor Wheels Online Prediction and Lifetime ExtensionDocument12 pages20 - Low-Cycle Fatigue of Turbocharger Compressor Wheels Online Prediction and Lifetime ExtensionlochtayNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument9 pagesSense OrgansЕкатерина КовальNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Hearing - EarsDocument3 pagesSense Organs: Hearing - EarstradagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesDigestive SystemImneil Jeanne Melendres-PerezNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissues: By: Bryce Pimentel, Bruce Pimentel, John Philip Pacho, Matthew ElacionDocument13 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues: By: Bryce Pimentel, Bruce Pimentel, John Philip Pacho, Matthew ElacionArchan Dom ReyesNo ratings yet
- VIII 13 SoundDocument16 pagesVIII 13 SoundBalaji ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms and AngiospermsDocument38 pagesGymnosperms and AngiospermsMeah PachecoNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan Soil SamplesDocument4 pagesScience Lesson Plan Soil SamplesColleenNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Light and Quantized EnergyDocument26 pages9.1 Light and Quantized EnergyMaricar Leonida BalbuenoNo ratings yet
- PhET - States of Matter in Html5Document3 pagesPhET - States of Matter in Html5Anonymous 52Z8ZFkvNo ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument13 pagesSound EnergyKu Ble YanNo ratings yet
- Birth of Quantum MechanicsDocument25 pagesBirth of Quantum MechanicsTejas DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Scotch College Science: The Universe & Our Changing EarthDocument37 pagesScotch College Science: The Universe & Our Changing EarthDavid WangNo ratings yet
- Classification of Animals and Plants PowerpointDocument14 pagesClassification of Animals and Plants Powerpointapi-455663521No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Patterns EvolutionDocument22 pagesPowerpoint Patterns Evolutionapi-289539870No ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations UnitDocument86 pagesAnimal Adaptations Unitapi-224842598No ratings yet
- Comets and AsteroidsDocument42 pagesComets and AsteroidsEd TapuroNo ratings yet
- CloningDocument6 pagesCloningkikkabuttigieg1466No ratings yet
- Sound Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSound Worksheet 1drz0mNo ratings yet
- Hearing and Sound Study SheetDocument4 pagesHearing and Sound Study Sheetapi-269680921No ratings yet
- Weather LectureDocument60 pagesWeather LecturenagtipunanNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: What Are The Sense Organs?Document3 pagesSensory Organs: What Are The Sense Organs?ajay kalangiNo ratings yet
- PowerpointDocument8 pagesPowerpointapi-254428474No ratings yet
- Light by AndrewDocument21 pagesLight by AndrewAndrew gadNo ratings yet
- Urogenital SystemDocument5 pagesUrogenital Systemstudent10100No ratings yet
- SoundDocument6 pagesSoundRanjini KulalNo ratings yet
- Stomach Digestion LabDocument2 pagesStomach Digestion Labapi-254428474No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemNo Name100% (1)
- The Ionic Product For WaterDocument6 pagesThe Ionic Product For WaterPrince SharmaNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton SkullDocument36 pagesAxial Skeleton SkulltiiandiNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDocument15 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits PPT 1-2Document36 pagesElectric Circuits PPT 1-2Fuego McFuegoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesParts of Nervous SystemCon PendonNo ratings yet
- Biological OrganizationDocument12 pagesBiological OrganizationSheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- AdaptationsDocument4 pagesAdaptationsJack BarkerNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument39 pagesAlternating CurrentRichard GomezNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Respiratory System For TodayDocument12 pagesOrgans of The Respiratory System For TodaySeptian PutraNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemIponla KarlChristianNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 Week 5 - 2021Document10 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 Week 5 - 2021Chelain Boucher100% (1)
- Punnet SquareDocument26 pagesPunnet SquarePrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- Sensory OrganDocument20 pagesSensory OrganJaneNo ratings yet
- Microscope BasicsDocument15 pagesMicroscope BasicsMark Arnold MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Lens & MirrorDocument8 pagesLens & Mirrordivya singh100% (1)
- Nervous System 2Document23 pagesNervous System 2TinNo ratings yet
- Uses of Mirrors and LensesDocument15 pagesUses of Mirrors and Lensesumi100% (1)
- 15 Parts of A FlowerDocument12 pages15 Parts of A FlowerGeorgina SunilNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Lab ReportDocument9 pagesCell Division Lab ReportBrianNo ratings yet
- Classification of AnimalDocument12 pagesClassification of AnimalMustika Ayuni100% (1)
- Life Cycle of A ButterflyDocument7 pagesLife Cycle of A ButterflyClarissa CruzNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument18 pagesHEATArtiNo ratings yet
- Sensory Pathway in ManDocument20 pagesSensory Pathway in ManKristienne Mae Sarmiento DiazNo ratings yet
- Microscope PDFDocument33 pagesMicroscope PDFSomesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Motion PowerpointDocument30 pagesMotion Powerpointapi-239426184100% (1)
- Week 15 Environmental Science Pollution and Its FactorsDocument22 pagesWeek 15 Environmental Science Pollution and Its FactorsReine Jholo BagaipoNo ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10Document40 pagesHeredity Class 10ChaithraNo ratings yet
- C++ NotesDocument11 pagesC++ NotesVedant AmonkarNo ratings yet
- Integrating Theory, Experiments, and FEA To Solve Challenging Nonlinear Mechanics ProblemsDocument17 pagesIntegrating Theory, Experiments, and FEA To Solve Challenging Nonlinear Mechanics ProblemsBodieTechNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Maths - Arithmetic ProgressionsDocument51 pagesClass 10 - Maths - Arithmetic ProgressionsgajulasureshNo ratings yet
- Lazauskas 2013Document15 pagesLazauskas 2013Youcef FermiNo ratings yet
- Electricity: ElectromagnetsDocument17 pagesElectricity: ElectromagnetsAyushJaiswalNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipe Riser PDFDocument8 pagesOffshore Pipe Riser PDFdndudcNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectabdul basitNo ratings yet
- Discovering Vanishing Objects in POSS I Red Images Using The Virtual Observatory - Beatrice - V - Stac1552Document12 pagesDiscovering Vanishing Objects in POSS I Red Images Using The Virtual Observatory - Beatrice - V - Stac1552Bozidar KemicNo ratings yet
- SharePoint 2010 QuestionsDocument5 pagesSharePoint 2010 QuestionsSreedhar KonduruNo ratings yet
- Isentropic ExponentDocument2 pagesIsentropic ExponentAlf OtherspaceNo ratings yet
- Abb Sas GeneralDocument43 pagesAbb Sas Generalsabill arasyidNo ratings yet
- Writing RectanglesDocument6 pagesWriting RectanglesVanessa LincolnNo ratings yet
- GGDocument8 pagesGGGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abacus PlusDocument4 pagesAbacus PlusPhương Chính NghĩaNo ratings yet
- PIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.2 (Mechanics) FinalDocument82 pagesPIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.2 (Mechanics) Finalsamarrana1234679No ratings yet
- What Is A ComputerDocument29 pagesWhat Is A ComputerRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Handheld Vital Signs Monitor: XH-30 SeriesDocument4 pagesHandheld Vital Signs Monitor: XH-30 SeriesTopan AssyNo ratings yet
- TMS Advanced TreeViewDocument64 pagesTMS Advanced TreeViewDanilo CristianoNo ratings yet
- Alex H.: Penguin ProjectDocument13 pagesAlex H.: Penguin Projectapi-504550016No ratings yet
- m1100 s12 v1.1f en - Fender - DesignDocument48 pagesm1100 s12 v1.1f en - Fender - Designdzul fiqarNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Exemplar PDFDocument130 pages12 Physics Exemplar PDFPRATIM SADHU100% (1)
- As 400Document70 pagesAs 400Radhakrishnan KandhasamyNo ratings yet
- Science July Assignment Grade 8Document3 pagesScience July Assignment Grade 8G PNo ratings yet
- Sarvani ProfileDocument12 pagesSarvani Profiledox4print100% (1)
- LEC# 15. Vapor Compression, Air ConditioningDocument31 pagesLEC# 15. Vapor Compression, Air ConditioningAhmer KhanNo ratings yet