Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Features of the Nose
Uploaded by
Muhammad Waqar UlfatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy and Features of the Nose
Uploaded by
Muhammad Waqar UlfatCopyright:
Available Formats
Presented By: Mian Naqib Jan Farman ullah
ANATOMICALLY NOSE IS DIVIDED AS EXTERNAL NOSE AND NASAL CAVITY ROOT DORSUM TIP ANTERIOR NARES NASAL SEPTUM COLUMELLA
Some features of external nose:
External nose is pyramidal in shape and maintained by skeletal framework External framework is made of bony and cartilaginous part Bony part are formed by nasal processes of frontal bone and ascending processes of the maxilla Cartilaginous part are formed by nasal cartilage and alar cartilages Skin over the external nose is thin in upper part and relatively thicker in lower part
Arterial supply of the external is from
Maxillary and opthalmic arteries
Nerve supply of external nose is from External nasal nerve Infratrochlear nerve Infraorbital nerve
Nasal cavity are two irregular cavities divided by nasal septum Nasal cavity is bounded by Floor Roof Medial wall Lateral wall
Floor is about 5cm long and 1.5 cm wide Floor is formed anteriorly by palatine process of maxilla and posteriorly by horizontal plate of palatine bone
Roof is about 7cm long and 1.5 wide Anterior slope is formed by nasal part of frontal bone and nasal cartilages Posterior slope is formed by inferior surface of body of sphenoid bone
Medial wall of nasal cavity is formed by nasal septum Nasal septum is formed by both bony and cartilaginous parts Bony part is mainly formed by Perpendicular plate of ethmoid above and vomer bone below and behind cartilaginous part is formed mainly by septal cartilage
Anterosuperior part is supplied by anterior ethmoidal artery Posteroinferior part is supplied by spenopalatine artery Anteroinferior part by the superior labial branch of facial artery Posterosuperior part by the greater palatine artery branch of 3rd part of maxillary artery
In the anteroinferior part of the nasal septum an anastamosis of arteries is present called kiessel Bachs plexus and the area is called little area The arteries taking part in this anastamosis are Sphenopalatine artery Greater palatine Superior labial branch of facial artery Anterior ethmoidal artery
Anterosuperior part is supplied by internal nasal branch of anterior ethmoidal nerve Anteroinferior part by anterior superior alveolar nerve Posteroinferior part by nasopalatine branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion Posterosuperior part by medial posterior nasal branches of pterygopalatine ganglion Special sensory nerve is olfactory confined to upper part
Lateral wall of nose is irregular due to presence of three shelf like projections called conchae Conchae are three in number Superior Middle Inferior Three meatus are present below each concha
Superior meatus contain the opening of posterior ethmoidal cells Middle meatus contians the opening of maxillary sinus, anterior and middle ethmoidal cells and frontal sinus Inferior meatus receives the nasal opening of nasolacrimal duct
Anterosuperior part by anterior ethmoidal artery Anteroinferior part by branches of facial and greater palatine arteries Posterosuperior part by sphenopalatine artery Posteroinferior part by branches from greater palatine artery
Anterosuperior part by anterior ethmoidal nerve-branch of ophthalmic nerve Anteroinferior part by superior alveolar nerve Posterosuperior part by superior lateral nasal branches from pterygopalatine ganglion Posteroinferior part by greater palatine branch from ptergopalatine ganglion
DEFINATION Nasal discharge refers to fluid that comes from the nose and originates in the nasal septum. NATURE. The nasal discharge may be clear,blood .it may contain mucous, pus .
Nasal discharge occurs due to the irritation of the lining nasal passages Foreign bodies Parasites Fungal infections Nasal tumor Allergic reactions
Accumulation of secretions Difficulty in breathing Decreased air flow through upper respiratory tract The patient may have loss of appetite Reverse sneezing may occur if the irritations extend to back of throat
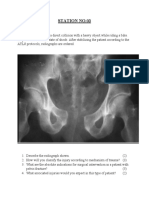
Nasal discharge is diagnosed by medical history and physical examination The cause of nasal discharge may be determined by diagnostic test Complete blood count [CBCs] Radiographs x rays of skull frequently required Rhinoscopy may help in the identification of nasal lesion Nasal biopsy can be performed
Antibiotics Antiparasitics Steroids Antifungal drugs
You might also like
- Paradise Lost1aDocument159 pagesParadise Lost1aAnonymous tlzqW7NNo ratings yet
- Lam Kam Chuen - Everyday Chi KungDocument205 pagesLam Kam Chuen - Everyday Chi KungJuan José100% (33)
- Puppy Sharing Agreement - Philippines Setting PDFDocument6 pagesPuppy Sharing Agreement - Philippines Setting PDFHannah HannahNo ratings yet
- B2B MARKETING DURING DOWNTURNSDocument5 pagesB2B MARKETING DURING DOWNTURNSRicha Mittal100% (1)
- Melee Weapons GuideDocument36 pagesMelee Weapons GuideKim100% (1)
- Upper Respiratory Tract AnatomyDocument61 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Anatomyيحيى اسماعيل الجميليNo ratings yet
- Basic Sinus AnatomyDocument71 pagesBasic Sinus AnatomyTalal AlanzyNo ratings yet
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery - Overview, Preparation, TechniqueDocument10 pagesFunctional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery - Overview, Preparation, TechniqueHendra SusantoNo ratings yet
- Hypopharyngeal Cancer Treatment OptionsDocument32 pagesHypopharyngeal Cancer Treatment OptionsDurrikamil khattakNo ratings yet
- HypoglycemiaDocument35 pagesHypoglycemiaMateen ShukriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EarDocument33 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of EarsuciNo ratings yet
- RTS1-K13-Anatomy of LungsDocument22 pagesRTS1-K13-Anatomy of LungsYohanna SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Seminar 1Document38 pagesMeningitis Seminar 1vani reddyNo ratings yet
- BERA Test Explained: What is Brainstem Evoked Response AudiometryDocument34 pagesBERA Test Explained: What is Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometryassumpta0% (1)
- Cancer LaryncDocument35 pagesCancer LaryncSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- CSOM Retroauricular FistulaDocument154 pagesCSOM Retroauricular FistulaM.rizki DestiantoroNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergency: James Paul O'NeillDocument43 pagesENT Emergency: James Paul O'NeillkylieverNo ratings yet
- Sailedinitis PDFDocument8 pagesSailedinitis PDFNavatha MorthaNo ratings yet
- Classifying and Treating Sinonasal TumorsDocument25 pagesClassifying and Treating Sinonasal TumorsMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Procedure GuideDocument18 pagesTracheostomy Procedure GuideSudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Assingment ON Ethical and Psychosocial Issues in Genetic TestingDocument17 pagesAssingment ON Ethical and Psychosocial Issues in Genetic TestingVaishali JainarainNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Cancer: Anatomy, Risk Factors, Staging and TreatmentDocument41 pagesLaryngeal Cancer: Anatomy, Risk Factors, Staging and TreatmentNidya PutriNo ratings yet
- 5 Asphyxia NeonetrumDocument27 pages5 Asphyxia NeonetrumRana VandanaNo ratings yet
- Airway Obstruction Final2Document33 pagesAirway Obstruction Final2Mahindra KumarNo ratings yet
- Practice Teaching Demonstration: Intracath InsertionDocument13 pagesPractice Teaching Demonstration: Intracath InsertionMegha lakra100% (1)
- Upper Airway ObstructionDocument17 pagesUpper Airway ObstructionRai Hana100% (1)
- The anatomy of the pharynxDocument15 pagesThe anatomy of the pharynxNina ZabrinaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Endocrine SystemMKDocument54 pagesHistology of Endocrine SystemMKDo Ra EmonNo ratings yet
- Tonsillectomy Slides 050427Document62 pagesTonsillectomy Slides 050427Aidiel FikriNo ratings yet
- Report EmpyemaDocument32 pagesReport EmpyemaMylah CruzNo ratings yet
- Nasal Foreign Bodies and Their ComplicationsDocument37 pagesNasal Foreign Bodies and Their ComplicationsnedvedcoxNo ratings yet
- Temp Bone Trauma Slides 051012Document55 pagesTemp Bone Trauma Slides 051012RaihanFarhanaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Operations and Procedures - CompleteDocument46 pagesObstetric Operations and Procedures - CompleteMax ZealNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument45 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementGeorge C. KasondaNo ratings yet
- POSTNATAL ASSESSMENT: Measuring Uterine Involution After DeliveryDocument18 pagesPOSTNATAL ASSESSMENT: Measuring Uterine Involution After DeliveryMiu MiuNo ratings yet
- Examining the Nose: Instruments and ProceduresDocument23 pagesExamining the Nose: Instruments and ProceduresKalyani TapreNo ratings yet
- Immunization Programme: National Health MissionDocument11 pagesImmunization Programme: National Health MissionAnimaNo ratings yet
- Constriction Band SyndromeDocument8 pagesConstriction Band SyndromesabistonNo ratings yet
- Measuring Central Venous Pressure: Elaine ColeDocument8 pagesMeasuring Central Venous Pressure: Elaine ColednllkzaNo ratings yet
- TRAUMATIC PPH PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENTDocument30 pagesTRAUMATIC PPH PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENTRizwana BanuNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Episiotomy and Nursing Management: 9.0 ObjectivesDocument8 pagesUnit 9 Episiotomy and Nursing Management: 9.0 ObjectivesSudip Kumar DeyNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis BK (LR)Document57 pagesTonsillitis BK (LR)Tiffany NurzamanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument27 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis MediaJoshua JayakaranNo ratings yet
- Lacrimal ApparatusDocument11 pagesLacrimal ApparatusmukulNo ratings yet
- Birthinjuries Dr.M.maniDocument65 pagesBirthinjuries Dr.M.manimaniNo ratings yet
- 63 Shock in Obstetrics & GynecologyDocument29 pages63 Shock in Obstetrics & GynecologyGodsonYeboah-AwudziNo ratings yet
- ANAT2341 Embryology: Early and Systemic Development: School of Medical SciencesDocument8 pagesANAT2341 Embryology: Early and Systemic Development: School of Medical SciencesJimson EchaveNo ratings yet
- Ectopicpregnancy Most ImpDocument79 pagesEctopicpregnancy Most Impﻣﻠﻚ عيسىNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument38 pagesRespiratory System Anatomyanju rachel jose100% (1)
- Diseases of The EarDocument48 pagesDiseases of The Earabela_amulu100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On PhysiologicalDocument22 pagesLesson Plan On PhysiologicalruchiNo ratings yet
- Tumors of External EarDocument10 pagesTumors of External Earsavin1996100% (2)
- Malpresentation and Malposition: Supervision By: DR Ashjan Tarayra Directed By: DR Montaser AsafrahDocument53 pagesMalpresentation and Malposition: Supervision By: DR Ashjan Tarayra Directed By: DR Montaser AsafrahMahmoud Asafrah100% (1)
- PneumothoraxDocument26 pagesPneumothoraxToni-Ann AllenNo ratings yet
- ENT Nursing Care GuideDocument32 pagesENT Nursing Care GuideabdulNo ratings yet
- Postmature Infants 1Document13 pagesPostmature Infants 1LyssaMarieKathryneEge100% (1)
- Otitis MediaDocument67 pagesOtitis MediaFurqan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Hypopharynx and LarynxDocument39 pagesAnatomy of the Hypopharynx and LarynxArjun NambiarNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL VENTILATION ASSIGNMENTDocument14 pagesMECHANICAL VENTILATION ASSIGNMENTNeha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Instrumental and Distructive DeliveryDocument66 pagesInstrumental and Distructive DeliveryDagnachew kasayeNo ratings yet
- Tracheobronchial TreeDocument51 pagesTracheobronchial TreeravishNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes in PregnancyDocument40 pagesPhysiological Changes in PregnancyArhum SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Fetal Skull Anatomy and Mechanisms of BirthDocument40 pagesFetal Skull Anatomy and Mechanisms of Birthsapana shah100% (1)
- Station 01Document2 pagesStation 01Muhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- USMLE 2013 BulletinDocument41 pagesUSMLE 2013 BulletinKarachibreezeNo ratings yet
- Station 03Document2 pagesStation 03Muhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- Station 06Document2 pagesStation 06Muhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Development of Pakistan Since 1947Document9 pagesConstitutional Development of Pakistan Since 1947Muhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- USMLE 2013 BulletinDocument41 pagesUSMLE 2013 BulletinKarachibreezeNo ratings yet
- Duplicate: Electricity BillDocument1 pageDuplicate: Electricity BillMuhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- Neonatal MeningitisDocument27 pagesNeonatal MeningitisMuhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire ThroidDocument1 pageQuestionnaire ThroidMuhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- Groin Hernias: Vic V. Vernenkar, D.O. St. Barnabas Hospital Bronx, NYDocument39 pagesGroin Hernias: Vic V. Vernenkar, D.O. St. Barnabas Hospital Bronx, NYMuhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- Surgery of Penis & UretraDocument81 pagesSurgery of Penis & UretraRiris SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi DAKLAK DienanhDocument14 pagesĐề Thi DAKLAK DienanhWin Trần Điển AnhNo ratings yet
- Ostenwold' A Complete Starter Town by Tom CartosDocument6 pagesOstenwold' A Complete Starter Town by Tom CartosRunic PinesNo ratings yet
- Kaylee Howlett ResumeDocument2 pagesKaylee Howlett Resumeapi-353201001No ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Questions AnswersDocument7 pagesExercise 1 Questions AnswersrosiNo ratings yet
- Create Races in 20 MinutesDocument8 pagesCreate Races in 20 MinutesRennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Infertility ACOGDocument8 pagesInfertility ACOGRifdaNo ratings yet
- Science Level 4 - Animal CardsDocument2 pagesScience Level 4 - Animal CardsClaudiaCarolinadeZeledónNo ratings yet
- Toxicology Reports: Rekhadevi Perumalla Venkata, Rajagopal SubramanyamDocument8 pagesToxicology Reports: Rekhadevi Perumalla Venkata, Rajagopal SubramanyamPoetri MarboenNo ratings yet
- Find The Temperature Using CricketsDocument2 pagesFind The Temperature Using CricketsMoreMoseySpeedNo ratings yet
- American Rabbit Breeders Association Guide (ARBADocument11 pagesAmerican Rabbit Breeders Association Guide (ARBANaniNo ratings yet
- Disney - Ice Age - The Movie Novel (KT) PDFDocument125 pagesDisney - Ice Age - The Movie Novel (KT) PDFMoyeen Uddin HasanNo ratings yet
- CT Mbbs by DR ShamolDocument197 pagesCT Mbbs by DR ShamolSiva Sandeep Chennimalai50% (2)
- Safety and First Aid Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesSafety and First Aid Test QuestionsYkay RoaringNo ratings yet
- OrgasmDocument20 pagesOrgasmnathanNo ratings yet
- H & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFDocument17 pagesH & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFRamin AmirkhiziNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ocean Animals Activity BookDocument5 pagesAdvanced Ocean Animals Activity BookRetno MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Organization of Nervous System: Anatomic DivisionsDocument2 pagesOrganization of Nervous System: Anatomic DivisionsDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Dani's Odyssey or Some Commotion in The Hinterland FogDocument228 pagesDani's Odyssey or Some Commotion in The Hinterland FogHanged Man PublishingNo ratings yet
- Creating A BOM From Scratch Ax 2012Document36 pagesCreating A BOM From Scratch Ax 2012Atul PrakashNo ratings yet
- CCDocument1 pageCCeelishorNo ratings yet
- Soal Vocabulary Part 2Document3 pagesSoal Vocabulary Part 2Sastrawan PelawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Using The Simple PresentDocument26 pagesChapter 3-Using The Simple PresentnoravintelerNo ratings yet
- Does Sastra Prescribes Animal Sacrifices For The Sake of ReligionDocument15 pagesDoes Sastra Prescribes Animal Sacrifices For The Sake of Religionkeshav3kashmiriNo ratings yet