Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emg Yagi-Uda Antenna
Uploaded by
Mohamad Azwan HussainOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Emg Yagi-Uda Antenna
Uploaded by
Mohamad Azwan HussainCopyright:
Available Formats
LECTURER: EN.
MUHAMAD HAFIZ BIN SHAFIE
GROUP MEMBER: MOHAMAD AZWAN B. HUSSAIN CT SHUHANA BINTI BAHAYAHKHI SAIDATUL RABIAH BINTI MD FADZIL HASMAH BT IBERAHIM DE100042 CE100150 CE090047 CE090134
The Yagi-Uda array was invented in 1926 by Shintaro Uda of Tohoku Imperial University, Japan, with a lesser role played by his colleague Hidetsugu Yagi. The work was originally done by Shintaro Uda, but published in Japanese. The work was presented for the first time in English by Yagi (who was either Uda's professor or colleague) who went to America and gave the first English talks on the antenna, which led to its widespread use.
Hence, even though the antenna is often called a Yagi antenna, Uda probably invented it. Its one of the most famous and used directional parasitic antennas.
A picture of Professor Yagi with a Yagi-Uda antenna
The Yagi-Uda antenna is
directional antenna
designed to maximize reception over long distances. Generating a much higher signal-to-noise ratio than other antenna designs, the Yagi-Uda antenna has become the de factor standard in antenna applications in almost all stationary applications utilizing frequencies above 10 MHz.
A Yagi-Uda antenna is familiar as the commonest kind of terrestrial TV antenna to be found on the rooftops of houses. It is usually used at frequencies
between about 30MHz and 3GHz, or a wavelength range
of 10 metres to 10 cm.
Yagi antenna usually used at frequencies between about 30MHz and 3GHz
This middle element is generically called the "driven element". This is because this is the only element that is connected directly to the radio, it actually drives the whole antenna.
The other two outer elements are generically called parasitic elements. One is called the Reflector and the other one is called the Director element.
These elements get their name from the job they do. The reflector reflects RF energy, the director directs RF energy.
Twin lead
Driven element with twin lead cable connection
Driven element with coaxial cable connection
The entire range of radiation covering the frequencies from 0 to approximately 10^23 hertz. In order of decreasing frequency the radiation goes, cosmic rays, gamma rays, x-rays, UV radiation, visible light, infrared radiation, microwaves, and radio waves.
The element of a Yagi-Uda array that is connected to the signal generator. The remaining elements are known as directors or reflectors.
A simple antenna with two equal length rods extending outward from each other in a straight line. When current passes through the dipole, radiation is emitted.
The element of a Yagi-Uda array that reflects the focused signal back toward the driven element.
The elements of a Yagi-Uda array that direct and focus the signal towards the driven element and reflector.
The distance it takes for a waveform to propagate one cycle.
The number of cycles a waveform completes in one second.
The measure of how much the signal is amplified by the antenna.
A term referring to electrical charge passing through a medium.
Refers to the current that is produced in a medium when that medium is exposed to a magnetic field (and the medium is not directly coupled with the magnetic field source).
In the field of antenna design the term radiation
pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the directional (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.
There is no magic circuit located inside the elements, they
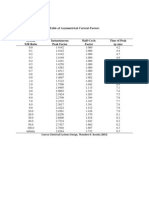
are simply straight rods! The reflector element is typically 5 % longer than the driven element and the director is typically 5 % shorted than the driven element.
Schematic of the operating principle of the original YagiUda
antenna for radio frequencies.
Signal comes in-phase
Yagi-Uda antenna pattern (2D)
Signal comes outphase
Signal comes out-phase
We can even add more directors elements to increase the gain.
Adding more reflector elements has NO more effect on the gain of the antenna.
Yagi-Uda antenna pattern (2D)
http://users.marktwain.net/aschmitz/anten
nas/calcantenna.html http://mapleleafcom.com/calculator_3elem ent_yagi.shtml
www.authorstream.com/Presentation/sahara
n49-605897-antenna-ppt/ www.hamuniverse.com/yagibasics.html en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yagi-Uda_antenna signalengineering.com/ultimate/yagi.html www.authorstream.com/Presentation/sachin sachin-180517-basic-antenna-theoryconcepts-entertainment-ppt-powerpoint/ mapleleafcom.com/calculator_3element_yag i.shtml www.changpuak.ch/electronics/yagi_uda_an tenna.php
You might also like
- Asymmetrical Current FactorsDocument1 pageAsymmetrical Current FactorsZaharah HalimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - System Protection PDFDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 5 - System Protection PDFMohamad Azwan Hussain100% (1)
- CHAPTER 6 Illumination PDFDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 6 Illumination PDFMohamad Azwan Hussain50% (2)
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Mohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- PR5 DDDocument11 pagesPR5 DDMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- Generation of HVDocument93 pagesGeneration of HVMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- Proceeding PaperDocument7 pagesProceeding PaperMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- My Proceeding Paper 1Document8 pagesMy Proceeding Paper 1Mohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- 3385 SchematicDocument1 page3385 SchematicMohamad Azwan Hussain100% (2)
- My Proceeding PaperDocument7 pagesMy Proceeding PaperMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- Steam TableDocument9 pagesSteam TableMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- Bex20903 Chapter 1 EmtDocument18 pagesBex20903 Chapter 1 EmtMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- Additional Handout Chapter1 Applied EMDocument13 pagesAdditional Handout Chapter1 Applied EMWaddah AbdoNo ratings yet
- Underwater Radio CommunicationDocument3 pagesUnderwater Radio CommunicationMohamad Azwan HussainNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Activity Tracker Wrist Band For Children Monitoring Using IOTDocument8 pagesActivity Tracker Wrist Band For Children Monitoring Using IOTAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- What Is 802.11?: 802.11 Networks For Dummies ProfessorsDocument4 pagesWhat Is 802.11?: 802.11 Networks For Dummies ProfessorsCORAL ALONSO JIMÉNEZNo ratings yet
- 1701 SIGFOX White Paper SecurityDocument10 pages1701 SIGFOX White Paper Securitysergio sergioNo ratings yet
- Jointech TrainingDocument15 pagesJointech TrainingGuy Fawkes100% (1)
- Zxr10 2900 SeriesDocument262 pagesZxr10 2900 SeriesShelton SizibaNo ratings yet
- 4 SDWAN ComponentsDocument2 pages4 SDWAN Componentssv23sNo ratings yet
- Wireshark OpnetDocument5 pagesWireshark OpnetOday RidhaNo ratings yet
- AAU5942 Technical Specifications (V100R016C10 - 02) (PDF) - ENDocument31 pagesAAU5942 Technical Specifications (V100R016C10 - 02) (PDF) - ENOndra Cizek100% (1)
- FirstDocument3 pagesFirstNaina GhoshNo ratings yet
- 8th 1st Q&ADocument17 pages8th 1st Q&AaddayesudasNo ratings yet
- Elenos Lowpower RenewableDocument20 pagesElenos Lowpower RenewableFRANK_357No ratings yet
- Latest Cisco EnsurePass CCNA 640 554 Dumps PDFDocument71 pagesLatest Cisco EnsurePass CCNA 640 554 Dumps PDFAbdel Rahman Jamil AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- S9300&S9300E V200R001C00 Hardware Description 05 PDFDocument282 pagesS9300&S9300E V200R001C00 Hardware Description 05 PDFmike_mnleeNo ratings yet
- Cisco SA 500 VPN Security Appliance & GreenBow IPSec VPN Client Software Configuration (English)Document14 pagesCisco SA 500 VPN Security Appliance & GreenBow IPSec VPN Client Software Configuration (English)greenbowNo ratings yet
- Anti Jamming of CdmaDocument10 pagesAnti Jamming of CdmaVishnupriya_Ma_4804No ratings yet
- Dell Emc Powerswitch S5200-On Series SwitchesDocument6 pagesDell Emc Powerswitch S5200-On Series SwitchesMortimer EchavarriaNo ratings yet
- KX-TA308: Telephone SystemDocument7 pagesKX-TA308: Telephone SystempipoNo ratings yet
- RTN 380 V100 Quick Installation Guide 01 PDFDocument32 pagesRTN 380 V100 Quick Installation Guide 01 PDFVanek505No ratings yet
- Aviatrix APIs For Datacenter ExtensionDocument5 pagesAviatrix APIs For Datacenter ExtensionSamiksha MittalNo ratings yet
- 10 - SurveyDocument54 pages10 - SurveyhazwanNo ratings yet
- CRM MaterialDocument153 pagesCRM MaterialGangadhar Reddy Tavva100% (1)
- BillDocument14 pagesBillvikramNo ratings yet
- Press Release - Samsung Service Van - Sylhet and Barishal - EnglishDocument1 pagePress Release - Samsung Service Van - Sylhet and Barishal - EnglishHamid KarzaiNo ratings yet
- APN of Different OperatorDocument2 pagesAPN of Different OperatorSmruti Ranjan DashNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik User ManagerDocument4 pagesMikrotik User ManagerpauliscirNo ratings yet
- 4-Servers and Storage Devices, Content ManagementDocument28 pages4-Servers and Storage Devices, Content Managementmalayajay.patel2021No ratings yet
- Trustworthy Ubiquitous Computing PDFDocument278 pagesTrustworthy Ubiquitous Computing PDFIron PeñaNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey On Wireless Sensor Networks: Pavlos Papageorgiou July 16, 2003Document17 pagesLiterature Survey On Wireless Sensor Networks: Pavlos Papageorgiou July 16, 2003Raghavendra RakeshNo ratings yet
- Readynas 3220/4220 Series Network Attached Storage (Nas)Document4 pagesReadynas 3220/4220 Series Network Attached Storage (Nas)Julio RodanesNo ratings yet
- China Mobile C2000Document9 pagesChina Mobile C2000badal2461318No ratings yet