Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blue Ocean Strategy
Uploaded by
makara1989Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blue Ocean Strategy
Uploaded by
makara1989Copyright:
Available Formats
8.
BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY
11 BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY
Dr. Waseso Segoro, Ir. MM.
IT TELKOM, APRIL 6, 2009
Kotler
Keller
10-2
10-3
10-4
10-5
10-6
BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY
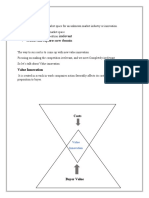
Creating product and services for which there are no direct competitors Managers should look beyond those boundaries to find uncoppied market positions that represent real value innovation
Designing creative business ventures to positively affect both a companys cost structure and its value proposition to consumers
10-7
10-8
10-9
10-10
Southwest Airlines created an airline that offer reliable, fun, and convinient service at a low cost
Callway Golf designed Big Bertha, a golf club with a large head and expanded sweet spot that helped golfers frustrated by the difficulty of hitting a golf ball squarely.
NetJets figured out to offer private jet service to a larger group of customers through fractional ownership
10-11
10-12
10-13
10-14
10-15
BOS - Formulation Principles
Reconstruct market boundaries
Focus on the big pictures not the numbers Reach beyond existing demand Get the strategic sequence right
10-16
BOS - Execution Principles
Overcome key organizational hurdles (Cognitive,Resource, Motivational,and Political - hurdles)
Build execution into strategy
10-17
10-18
10-19
8. PLC STRATEGY DEVELOPMENT
10 Product Life Cycle
Dr. Waseso Segoro, Ir. MM.
IT TELKOM, APRIL 6, 2009
Kotler
Keller
Chapter Questions
What marketing strategies are appropriate at each stage of the product life cycle?
What are the implications of market evolution for marketing strategies?
10-21
Market Evolution Stages
Emergence, before a market materializes, it exists as a latent market. On launching the product, the emergence stage begins.
Growth, if the new product sells well, new firms will enter the market, ushering in a market growth stage. Maturity, eventually competitors cover and serve all the major market segments and the market enters the maturity stage. Decline, demand for the present products will begin to decrease and the market will enter the decline stage.
10-22
Product Life Cycle
Introduction, a period of slow sales growth
Growth, a period of rapid market acceptance and substatial profit improvement Maturity, a slowdown in sales growth Decline, sales show a downward drift and profits erode
10-23
10-24
Facts about Life Cycles
Products have a limited life.
Product sales pass through distinct stages, challencges, opportunity, problem to the seller Profits rise and fall at different stages. Products require different marketing, financial, manufacturing, purchasing, and human resource strategies in each stage.
10-25
10-26
10-27
10-28
10-29
Marketing Program Modifications
Prices, would a price cut attract new buyers?
Distribution, can more outlets be penetrated? Advertising, should advertising expenditures be increased?
Sales promotion, should the company step up the promotion?
Services, can the company speed up delivery?
10-30
10-31
3-32
10-33
10-34
10-35
10-36
10-37
NEXT WEEK GROUP ASSIGNMENT
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE : DO BRANDS HAVE FINITE LIVES? PLEASE CHOOSE ANY BRAND
10-38
You might also like
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument21 pagesBlue Ocean Strategyjoe100% (5)
- Final Requirements - Case Study AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinal Requirements - Case Study Analysisfretchi candonesNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy PresentationDocument25 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy PresentationhappysinNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy PresentationDocument25 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy PresentationManpreet Singh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy Concept - Overview & Analysis: Achieve success through innovation and make the competition irrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy Concept - Overview & Analysis: Achieve success through innovation and make the competition irrelevantRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- Entrep PresentationDocument16 pagesEntrep PresentationJohn rainier BoteroNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument28 pagesBlue Ocean Strategylorinevaz100% (5)
- Entrep PresentationDocument16 pagesEntrep PresentationJohn rainier BoteroNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument21 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyRahul MurarkaNo ratings yet
- Blue and Red Ocean StrategyDocument6 pagesBlue and Red Ocean Strategyjack martinNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy Vs Red Ocean StrategyDocument37 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy Vs Red Ocean StrategySAYED FARAZ ALI SHAHNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument36 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesAjeeb RafeekahammedNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Creating New Products and ServicesDocument39 pagesModule 8 Creating New Products and ServicesBruno SaturnNo ratings yet
- SM Assignment 5Document7 pagesSM Assignment 5Gaurav SonkeshariyaNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument36 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesnagarajanNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument36 pagesProduct Life CycleMuhammad Shahinur IslamNo ratings yet
- Hofers DPMDocument39 pagesHofers DPMramansharmachdNo ratings yet
- Submitted To Submitted By: Contemporary Issue OnDocument23 pagesSubmitted To Submitted By: Contemporary Issue OnnmortynNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy4875Document19 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy4875Kamalakannan Annamalai100% (1)
- A.D PresentatnDocument20 pagesA.D PresentatnMinakshee KumariNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy Literature Reviewc5rr5sqw100% (1)
- Group 4 Strategic PPT Blue OceanDocument30 pagesGroup 4 Strategic PPT Blue OceanChristous PkNo ratings yet
- PLC Model of Kit Kat Caramel CrunchyDocument6 pagesPLC Model of Kit Kat Caramel CrunchyJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy - PresentationDocument29 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy - PresentationRohit Ghai100% (1)
- CHP 6 - BCG - Blue Ocean StrategyDocument19 pagesCHP 6 - BCG - Blue Ocean StrategyBBHR20-A1 Wang Jing TingNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocearn Strategy 15178 142Document19 pagesBlue Ocearn Strategy 15178 142Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy Against Business Model InnovationDocument14 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy Against Business Model Innovationfalsowaidi880No ratings yet
- The PMS MapDocument6 pagesThe PMS MapAhmed KumarNo ratings yet
- The Blue Ocean Strategy: W. Chan Kim & Renée MauborgneDocument47 pagesThe Blue Ocean Strategy: W. Chan Kim & Renée MauborgneKamalakannan AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument4 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyDebarati ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Bab 6Document26 pagesStrategic Management Bab 6Vemiastri MulyonoNo ratings yet
- Evaluate The Business Model of A CompanyDocument13 pagesEvaluate The Business Model of A CompanySundaresan SabanayagamNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing - Blue Ocean Strategy 07Document28 pagesPrinciples of Marketing - Blue Ocean Strategy 07Darwyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle StagesDocument4 pagesProduct Life Cycle StagesShruti TopraniNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocearn StrategyDocument19 pagesBlue Ocearn StrategyMansoor AliNo ratings yet
- Innovation Strategy S3Document64 pagesInnovation Strategy S3Sumit Sharma100% (1)
- MGT 502. Business Strategy, Social Resposibility and SustainabilityDocument22 pagesMGT 502. Business Strategy, Social Resposibility and SustainabilityBaken D DhungyelNo ratings yet
- Irrelevant Creates and Captures New Domain: Blue Ocean StrategyDocument7 pagesIrrelevant Creates and Captures New Domain: Blue Ocean StrategyMusfira FatimaNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument14 pagesStrategic ManagementMAXWELL gwatiringaNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy: Create Uncontested Market Space & Make The Competition IrrelevantDocument21 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy: Create Uncontested Market Space & Make The Competition IrrelevantKadir Yıldırım100% (2)
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument4 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyshoaibqadriNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Quick IntroductionDocument26 pagesBlue Ocean Quick IntroductionJohn WaweruNo ratings yet
- Harsh Bus 815 AssignmentDocument11 pagesHarsh Bus 815 Assignmentasogba segunNo ratings yet
- The Blue Ocean StrategyDocument8 pagesThe Blue Ocean StrategybrendaNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document11 pagesReport 1Roselyn MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument17 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyRaman Deep ChambalNo ratings yet
- Getting Routes To Market Right PDFDocument16 pagesGetting Routes To Market Right PDFAnonymous 45z6m4eE7pNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 - Business Policy and StrategyDocument23 pagesChapter-6 - Business Policy and Strategybyomkesh bakshiNo ratings yet
- Report - BLUE OCEAN STRATEGYDocument19 pagesReport - BLUE OCEAN STRATEGYLejani QuiochoNo ratings yet
- Implementing Target CostingDocument31 pagesImplementing Target CostingJonnattan MuñozNo ratings yet
- Hamza Amin MSBA 018Document3 pagesHamza Amin MSBA 018Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument2 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyRemus Romano ReyesNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Vs Red Ocean StrategyDocument62 pagesBlue Ocean Vs Red Ocean StrategyRobbi WanNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis Through Life Cycle Analysis and Target CostingDocument35 pagesCost Analysis Through Life Cycle Analysis and Target CostingSunny KhsNo ratings yet
- BCG Classics TheoriesDocument18 pagesBCG Classics TheoriesSHALINI ARYA-IBNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Ojambo Paul 160-500Document7 pagesStrategic Management Ojambo Paul 160-500paulojambo91No ratings yet
- Discount Business Strategy: How the New Market Leaders are Redefining Business StrategyFrom EverandDiscount Business Strategy: How the New Market Leaders are Redefining Business StrategyNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: Launch of a laundry liquid detergent in Sri LankaFrom EverandModel Answer: Launch of a laundry liquid detergent in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Innovator's Dilemma: by Clayton M. Christensen | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Innovator's Dilemma: by Clayton M. Christensen | Includes AnalysisNo ratings yet
- The Customer Catalyst: How to Drive Sustainable Business Growth in the Customer EconomyFrom EverandThe Customer Catalyst: How to Drive Sustainable Business Growth in the Customer EconomyNo ratings yet
- House DesignsDocument25 pagesHouse DesignsmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Novena TO Our Mother OF Perpetual Help: (Wednesday)Document58 pagesNovena TO Our Mother OF Perpetual Help: (Wednesday)mdesreal100% (1)
- Novena For The Dear Dead-FemaleDocument2 pagesNovena For The Dear Dead-FemaleFilipino Ministry Council100% (17)
- Novena For The Dear Dead-FemaleDocument2 pagesNovena For The Dear Dead-FemaleFilipino Ministry Council100% (17)
- Access To Capital in Rural Thailand: An Estimated Model of Formal vs. Informal CreditDocument41 pagesAccess To Capital in Rural Thailand: An Estimated Model of Formal vs. Informal CreditmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document506 pagesPresentation 1mdesrealNo ratings yet
- Yoga Postures Yogasanas PDFDocument59 pagesYoga Postures Yogasanas PDFAndy DragomirNo ratings yet
- Doing Business 2013Document282 pagesDoing Business 2013mdesrealNo ratings yet
- IC Recorder: Operating InstructionsDocument121 pagesIC Recorder: Operating InstructionsmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Postal and Courier ServicesDocument3 pagesPostal and Courier ServicesmdesrealNo ratings yet
- UnionPostale Jan Mar2013Document28 pagesUnionPostale Jan Mar2013mdesrealNo ratings yet
- Ikea Catalogue enDocument163 pagesIkea Catalogue enmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Forbes Forecasts and Market EstimatesDocument5 pagesForbes Forecasts and Market EstimatesmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Yoga Postures Yogasanas PDFDocument59 pagesYoga Postures Yogasanas PDFAndy DragomirNo ratings yet
- Yoga To Strengthen BackDocument8 pagesYoga To Strengthen BackmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Forbes Forecasts and Market EstimatesDocument5 pagesForbes Forecasts and Market EstimatesmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Forbes Forecasts and Market EstimatesDocument5 pagesForbes Forecasts and Market EstimatesmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Ikea Catalogue enDocument163 pagesIkea Catalogue enmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Tariff & Customs Code Vol 2Document73 pagesTariff & Customs Code Vol 2cmv mendoza100% (10)
- How Is Big Data Faring in The Enterprise?Document3 pagesHow Is Big Data Faring in The Enterprise?mdesrealNo ratings yet
- BillMelindaGatesFoundation FinancialServicesForPoorStrategyNov10Document12 pagesBillMelindaGatesFoundation FinancialServicesForPoorStrategyNov10mdesrealNo ratings yet
- Yoga To Strengthen BackDocument8 pagesYoga To Strengthen BackmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Calculate GrowthDocument5 pagesCalculate GrowthbhaskarnisNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal SystemsDocument12 pagesPerformance Appraisal SystemsmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Motivatecreate McGuinnessDocument58 pagesMotivatecreate McGuinnessmdesrealNo ratings yet
- Blueprint Obooko Mind0012Document138 pagesBlueprint Obooko Mind0012mdesrealNo ratings yet