Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shoulder Joint
Uploaded by
quadpumperOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shoulder Joint
Uploaded by
quadpumperCopyright:
Available Formats
The Shoulder Joint (Glenohumeral Joint)
What bones make up the shoulder joint?
Clavicle
Scapula
Humerus
Joint involved
The shoulder joint is made up of the glenohumeral joint. This is an enarthrodial, or multiaxial, ball and socket joint. It is very mobile, but sacrifices stability.
The Shoulder Joint
Many variable movements occur at the shoulder. Movement of the humerus usually involves movement at the shoulder girdle, known as scapulohumeral rhythm.
What are the 8 movements that occur at the shoulder joint? Abduction Adduction Flexion Extension
Horizontal abduction Internal Rotation Horizontal adduction External Rotation
Shoulder Girdle Movements
Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Joint What shoulder joint (glenohumeral) motions occur with each shoulder girdle (scapular) motion?
Protraction
Retraction Upward Rotation
Horizontal Adduction Horizontal Abduction Abduction Adduction
Shoulder shrug Shoulder depression
Downward Rotation Elevation
Depression
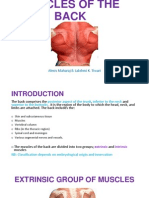
The Shoulder Joint
To study the 9 muscles of the shoulder joint, we will break them into intrinsic and extrinsic groups. The intrinsic group originate on the clavicle and scapula. What are the 7 intrinsic muscles of the shoulder joint?
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Subscapularis Deltoid
Teres minor
Coracobrachialis Teres major
The Shoulder Joint
What are the two extrinsic muscles of the shoulder joint?
Latissimus dorsi Pectoralis major
Intrinsic muscles of the shoulder joint
The first group of intrinsic muscles are the SITS muscles. The band of tendons of these four muscles compose the rotator cuff of the shoulder joint. The functions of the SITS muscles include rotation of the humerus, and to provide stability, especially against subluxation.
Rotator Cuff
Supraspinatus
The Shoulder Joint
A. Supraspinatus muscle - This muscle is most superior of the rotator cuff. It pulls the head of the humerus into the glenoid fossa to initiate abduction and provide an effective angle of pull for the deltoid. It helps reinforce the shoulder joint.
Actions - assist abduction, stabilize head of humerus
The Shoulder Joint
Testing the supraspinatus for injury
1. Resisting against abduction - if the patient has trouble abducting the arm against resistance and tries to substitute the scapular muscles, it can indicate supraspinatus damage.
2. Drop arm test - if the patient can not slowly lower the arm from an abducted position, it can indicate supraspinatus injury.
Infraspinatus
The Shoulder Joint
B. Infraspinatus muscle - located just inferior to the supraspinatus, it also helps reinforce the shoulder capsule and stabilize the humerus during abduction. Actions of the infraspinatus External rotation - most powerful external rotator of SITS muscles Extension of humerus Horizontal abduction
The Shoulder Joint
Exercises involving the infraspinatus Chinning, dips, rope climbing. Any exercise in which the arms are pulled down forcefully. Works in conjunction with teres major and latissimus dorsi. Testing of the infraspinatus muscle External rotation against resistance. Patient lays prone with arm hanging. Fixate the scapula and have them rotate up against resistance.
Teres Minor
The Shoulder Joint
C. Teres minor - Inferior to the infraspinatus, this muscle also reinforces the shoulder capsule and helps stabilize the head of the humerus during abduction.
Actions of the teres minor External rotation Horizontal abduction
Extension
The Shoulder Joint
Exercises to strengthen the teres minor
Same as infraspinatus - chinning, rope climbing, dips, any movement in which arms go down forcefully. Testing the teres minor
Same test as for infraspinatus, prone test for external rotation with scapula stabilized.
Subscapularis
The Shoulder Joint
D. Subscapularis - the final muscle in the four rotator cuff muscles. As with the others, helps stabilize shoulder capsule. This is the only rotator cuff muscle to originate on the anterior surface of the scapula.
Actions of the subscapularis Internal rotation - main action Adduction Extension - from flexed position
The Shoulder Joint
Exercises involving the subscapularis As with infraspinatus and teres minor, it is involved in chinning, dips and rope climbing.
A specific exercise for this muscle is internal rotation against resistance.
Testing the subscapularis Similar to other muscles, have the patient lay prone, and internally rotate against resistance.
Deltoid
Shoulder Joint Muscles
Additional Intrinsic Muscles
A. Deltoid Muscle - This muscle forms the rounded muscle bulk of the shoulder joint. It is a strong abductor, but cannot initiate that movement because the angle of pull is parallel to the humerus when the arm is by the side. Recall that the supraspinatus initiates the movement.
The deltoid muscle is divided into three portions, and hence is sometimes called deltoids muscle. The three portions are anterior, middle, and posterior.
Shoulder Joint Muscles
What are the actions of the anterior deltoid? Abduction Internal rotation
Horizontal adduction
Flexion
What are the actions of the middle deltoid? Abduction What are the actions of the posterior deltoid? Abduction External rotation Horizontal abduction Extension
Shoulder Joint Muscles
Exercises to strengthen the deltoid muscle Bench press Overhead press Front arm raise
Lateral arm raise
Prone flies
Supine horizontally adducted dumbbell raises will strengthen the anterior deltoid. Prone horizontally abducted dumbbell raises will strengthen the posterior deltoid
Coracobrachialis (not brachialis)
Shoulder Joint Muscles
B. Coracobrachialis muscle - This muscle is named for its origin and insertion. What actions does the coracobrachialis perform? Adduction Flexion Horizontal Adduction Exercises to strengthen would include: Bench press Supine flies Lat pulls Not particularly strong, most functional in Horizontal Adduction
Teres Major
Shoulder Joint Muscles
C. Teres Major muscle - Together with the infraspinatus and teres minor, it helps stabilize the humerus during abduction. It is also known as the latissimus dorsis little helper. What are the actions of the teres major? Adduction Internal Rotation Extension
Shoulder Joint Muscles
Exercises to strengthen the teres major muscle Rope climbing Lat pulls
Internal rotation against resistance As with the coracobrachialis, this muscle is not very powerful on its own.
Shoulder Joint Muscles
D. Latissimus dorsi latissimus means widest & dorsi means back (Latin). Powerful in adduction, extension and internal rotation of humerus. Powerful contraction in chinning. Assisted in all actions by teres major. What are the actions of the latissimus dorsi? Adduction Internal Rotation Horizontal abduction Extension
Latissimus Dorsi
Shoulder Joint Muscles
What are some activities involving or strengthening the Latissimus dorsi? Lat pull downs Dips Chinning Rope climbing Pull over
Rowing
Pectoralis Major
Shoulder Joint Muscles
E. Pectoralis Major (pectus, breast bone) works closely with anterior deltoid. It is divided into upper and lower sections. Actions of Pectoralis Major Upper fibers (clavicular head): internal rotation, horizontal adduction, some flexion, some abduction
Lower fibers (sternal head): internal rotation, horizontal adduction, extension, some adduction
Shoulder Joint Muscles
Exercises or activities involving the pectoralis major? Bench press
Pull ups
Push ups
Dumbell flies
Incline press Decline press
Incline press muscles combine bench & overhead presses. Decline press made up of bench press & the dip.
Shoulder Joint Muscles
Biceps brachii (short and long heads) originate on the scapula and insert on the radius. It crosses two joints. Short head assists flexion, adduction; Long assists with abduction. Triceps brachii (long head) originates on the scapula just below the glenoid fossa. It assists with shoulder extension and adduction.
Shoulder Joint Injuries
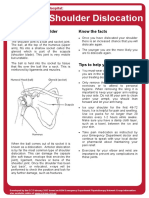
Dislocation: the head of the humerus is pushed out of the glenoid fossa. The glenohumeral joint is the most commonly dislocated joint in the body. Rotator cuff damage: this is the most common disorder of the shoulder. Supraspinatus is most commonly injured.
Shoulder Joint Injuries
Rotational injuries: tears of the labrum, the rotator cuff muscles, and the biceps brachii tendon among injuries resulting from repeated, forceful rotation at shoulder. Tears of rotator cuff attributed to extreme tension during deceleration phase of throwlike motion. Subscapular neuropathy: compression of subscapular nerve.
You might also like
- 5 Senior ExercisesDocument3 pages5 Senior Exercisestamaki55No ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder Phase 2ExorLive-WorkoutDocument2 pagesFrozen Shoulder Phase 2ExorLive-WorkoutJomari ServanoNo ratings yet
- Frozen ShoulderDocument4 pagesFrozen ShoulderFirza OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Upper and Lower Limb: A Systems ApproachDocument52 pagesGross Anatomy of The Upper and Lower Limb: A Systems ApproachcoolsuernameNo ratings yet
- Fitness Training: 5 Elements of A Rounded RoutineDocument11 pagesFitness Training: 5 Elements of A Rounded RoutinefrnildegaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Shoulder DislocationDocument2 pagesAnterior Shoulder DislocationcilengsaiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnDocument60 pagesStructure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Www.gymstick.comDocument52 pagesWww.gymstick.comsul1nko100% (1)
- Physiotherapy Exercises Following Transfemoral (Above Knee) AmputationDocument5 pagesPhysiotherapy Exercises Following Transfemoral (Above Knee) AmputationLuqmanul HakimNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument47 pagesMuscular SystemKrystal Kaye AczonNo ratings yet
- Knee ScopeDocument3 pagesKnee ScopeSherri Shulamit TerebishNo ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder PreventionDocument4 pagesFrozen Shoulder PreventionDavid MarcksNo ratings yet
- SI Provocative TestsDocument7 pagesSI Provocative TestsGumDrop100% (1)
- Frozen Shoulder RevisedDocument17 pagesFrozen Shoulder Revisednerissa arvianaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument38 pagesMuscles of The BackPrashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Soothe Sciatic Sequence 1Document11 pagesSoothe Sciatic Sequence 1Akash SinghviNo ratings yet
- Toe Touch ProgressionDocument1 pageToe Touch Progressionses1984205No ratings yet
- Exercise and Myasthenia Gravis (MG)Document3 pagesExercise and Myasthenia Gravis (MG)sridhar_physioNo ratings yet
- Chest and TricepsDocument7 pagesChest and TricepstareqNo ratings yet
- The Functional Anatomy of Tensor Fascia Latae and Gluteus Medius and Minimus. Janat00044-0181Document11 pagesThe Functional Anatomy of Tensor Fascia Latae and Gluteus Medius and Minimus. Janat00044-0181Itai IzhakNo ratings yet
- Examination of ElbowDocument18 pagesExamination of Elbowharmohit singhNo ratings yet
- Plantar Fasciitis - A Self Help GuideDocument8 pagesPlantar Fasciitis - A Self Help GuideAjmera HarshalNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation: Walking After Total Knee ReplacementDocument10 pagesRehabilitation: Walking After Total Knee ReplacementSandeep DhimanNo ratings yet
- Knee, Ankle and Foot Joint MobilizationDocument17 pagesKnee, Ankle and Foot Joint MobilizationLokesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- GRASP All 3 Levels11490 PDFDocument115 pagesGRASP All 3 Levels11490 PDFAmit ZalaNo ratings yet
- Basic BiomechanicsDocument54 pagesBasic BiomechanicsStevenDanielNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Thoracic Outlet Syndrome PDFDocument8 pagesExercises For Thoracic Outlet Syndrome PDFmyhobby_roNo ratings yet
- Delta Fitness: Elbow Bursitis (Olecranon Bursitis)Document2 pagesDelta Fitness: Elbow Bursitis (Olecranon Bursitis)Jomari ServanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 1 Vertebral Motion DynamicsDocument67 pagesLecture No. 1 Vertebral Motion DynamicsSYED ALI HUSSAIN100% (1)
- ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation GuidelinesDocument4 pagesACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Guidelinesfia0711No ratings yet
- Biology SkeletonDocument36 pagesBiology SkeletonHariPriya JothimeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Passive Scapular Adduction TestDocument15 pagesPassive Scapular Adduction Testapi-468597987No ratings yet
- Efficacy of Neck Stabilization Exercises For Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled StudyDocument6 pagesEfficacy of Neck Stabilization Exercises For Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled StudyAnonymous mWAaDZmlJwNo ratings yet
- Angle or Pull of MuscleDocument13 pagesAngle or Pull of MuscleSneh KevadiyaNo ratings yet
- RNT Deep Squat Trunk Flexion CorrectionDocument1 pageRNT Deep Squat Trunk Flexion Correctionses1984205No ratings yet
- 9 Pregnancy Stretches For The Whole Body 4 Pager Apr17 v3Document4 pages9 Pregnancy Stretches For The Whole Body 4 Pager Apr17 v3LeiltonNo ratings yet
- What Is Biceps Tendonitis?Document5 pagesWhat Is Biceps Tendonitis?Nishant RajaNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy and Frozen ShoulderDocument7 pagesPhysiotherapy and Frozen Shoulderdeepa1982No ratings yet
- Tendon Neuroplastic TrainingDocument9 pagesTendon Neuroplastic TrainingLara VitorNo ratings yet
- Generic Shoulder Physiotherapy Exercises Sheet: Information For Patients Orthopaedic Shoulder ServiceDocument16 pagesGeneric Shoulder Physiotherapy Exercises Sheet: Information For Patients Orthopaedic Shoulder ServiceBence KlusóczkiNo ratings yet
- AIS and YogaDocument3 pagesAIS and Yogasale18No ratings yet
- Hip Joint PDFDocument11 pagesHip Joint PDFStephen Subiera MiayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Derived PositionsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Derived PositionsEmad Eldin Mohamed Abdelatief100% (1)
- MusclesDocument66 pagesMusclesusernameNo ratings yet
- Angle of Pull and Pulley by Hamza MirDocument25 pagesAngle of Pull and Pulley by Hamza MirAmeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Shoulder ExercisesDocument3 pagesFundamental Shoulder ExercisesRui CunhaNo ratings yet
- Frozen ShoulderDocument1 pageFrozen ShouldersyndyeNo ratings yet
- Muscular Strength and Endurance:: WEEK 2 (Final Term)Document6 pagesMuscular Strength and Endurance:: WEEK 2 (Final Term)Hey itsJamNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument72 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyJoie UrsalNo ratings yet
- Scap ExerDocument2 pagesScap Exerw_ramirez94No ratings yet
- Mat ActivitiesDocument2 pagesMat ActivitiesAtul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hip JointDocument25 pagesHip JointHashim OmarNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint: Important PointsDocument4 pagesHip Joint: Important PointsNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Faradic Foot Bath & Faradism Under PressureDocument6 pagesFaradic Foot Bath & Faradism Under PressureNamrathaThalatoti ywSSAmHsULNo ratings yet
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCLR) Rehabilitation ProtocolDocument19 pagesPosterior Cruciate Ligament (PCLR) Rehabilitation ProtocolosamadrNo ratings yet
- Starting PositionsDocument60 pagesStarting Positionsheer rehman100% (1)
- Shoulder GirdleDocument32 pagesShoulder GirdletdbamaboyNo ratings yet
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesFrom EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesNo ratings yet
- Dead LiftsDocument8 pagesDead LiftsjwarswolvesNo ratings yet
- Tai Chi IDocument1 pageTai Chi IquadpumperNo ratings yet
- FoolDocument1 pageFoolquadpumperNo ratings yet
- Hafiz Poems - BilingualDocument404 pagesHafiz Poems - BilingualAmir Khorasani100% (1)
- School Be3 BDocument1 pageSchool Be3 BquadpumperNo ratings yet
- Concrete Super Structure ReportDocument43 pagesConcrete Super Structure ReportLivian TeddyNo ratings yet
- MSDS DowthermDocument4 pagesMSDS DowthermfebriantabbyNo ratings yet
- Bagpipe LV 1-5Document228 pagesBagpipe LV 1-5Sathia Kdms100% (2)
- T.A.T.U. - Waste Management - Digital BookletDocument14 pagesT.A.T.U. - Waste Management - Digital BookletMarieBLNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument14 pagesProject ReportNoah100% (7)
- Badminton ReviewerDocument10 pagesBadminton ReviewerHailsey WinterNo ratings yet
- Data SiEMEx School SafetyPreparedness 25 26 NOVDocument81 pagesData SiEMEx School SafetyPreparedness 25 26 NOVSuraj RajuNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewerDocument3 pagesMMW ReviewerMarcSaloj NeryNo ratings yet
- Carrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyDocument2 pagesCarrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyVineet JogalekarNo ratings yet
- Prevailing Torque Locknut Technical SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPrevailing Torque Locknut Technical SpecificationsLiu YangtzeNo ratings yet
- PH & TemperatureDocument8 pagesPH & TemperatureNanaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium SeriesDocument4 pagesManual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium Seriesfosavo5839No ratings yet
- Assessment of Diabetic FootDocument7 pagesAssessment of Diabetic FootChathiya Banu KrishenanNo ratings yet
- Bardonna MenuDocument16 pagesBardonna MenuFarley ElliottNo ratings yet
- Quartile1 PDFDocument2 pagesQuartile1 PDFHanifah Edres DalumaNo ratings yet
- 1n5711 RF Detector Diode 70v PIV DatasheetDocument3 pages1n5711 RF Detector Diode 70v PIV DatasheetgordslaterNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biomechanics: Leigh W. Marshall, Stuart M. McgillDocument4 pagesClinical Biomechanics: Leigh W. Marshall, Stuart M. McgillMichael JunNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 11 NotesDocument26 pagesPhysics Unit 11 Notesp.salise352No ratings yet
- Clinical Reviews: The Management of Children With Gastroenteritis and Dehydration in The Emergency DepartmentDocument13 pagesClinical Reviews: The Management of Children With Gastroenteritis and Dehydration in The Emergency DepartmentRina Dewi AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Paper-Czechowski-Slow-strain-rate Stress Corrosion Testing of Welded Joints of Al-Mg AlloysDocument4 pagesPaper-Czechowski-Slow-strain-rate Stress Corrosion Testing of Welded Joints of Al-Mg Alloysjavo0128No ratings yet
- Iodide and Bromide Ions in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines D 3869 - 04Document12 pagesIodide and Bromide Ions in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines D 3869 - 04stevgonNo ratings yet
- Child DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChild Development4AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Flow Zone Indicator Guided Workflows For PetrelDocument11 pagesFlow Zone Indicator Guided Workflows For PetrelAiwarikiaar100% (1)
- 1.1.3.12 Lab - Diagram A Real-World ProcessDocument3 pages1.1.3.12 Lab - Diagram A Real-World ProcessHalima AqraaNo ratings yet
- Contoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HidupDocument2 pagesContoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HiduprusmansyahNo ratings yet
- G10Mapeh Exam First QuaterDocument8 pagesG10Mapeh Exam First QuaterJonas LamcisNo ratings yet
- Chillers VoltasDocument4 pagesChillers Voltasanil shuklaNo ratings yet
- Ap, Lrrsisal of Roentgenograph, Ic: I SsayDocument30 pagesAp, Lrrsisal of Roentgenograph, Ic: I SsayMindaugasStacevičiusNo ratings yet
- Automatic Train OperationDocument6 pagesAutomatic Train OperationAnupam KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 08 - 2061 USTR 2222a (1) Supor EKVDocument24 pages08 - 2061 USTR 2222a (1) Supor EKVHassan Houdoud0% (1)